The main purpose of fire doors is to provide conditions for quick evacuation of people from a burning building and effective work of the Emergencies Ministry employees to localize and extinguish the fire. Based on this, the places of mandatory installation of such structures are determined. In accordance with the rules established by the current regulatory framework, fire doors must be installed in two main cases - on the escape routes in crowded places and at the entrance to premises or buildings with an increased level of fire hazard.
Where should fire doors be installed?
The current regulatory enactments regulate the places where special doors must be installed, as well as the requirements for structures. Basic documents indicating where installation is required:
- SNiP 21-01-97. Standards for the installation of all fire protection structures.
- No. 123-FZ. Contains the Technical Regulations, which describe the fire safety requirements in relation to the facilities in operation and under construction.
- SP 1.13130.2009. Rules describing current fire protection systems, exits and escape routes.
List of objects where installation is required:
- ventilation chambers;
- niches for communications and equipment;
- production facilities (warehouses, workshops, utility rooms);
- warehouses with combustible and flammable materials;
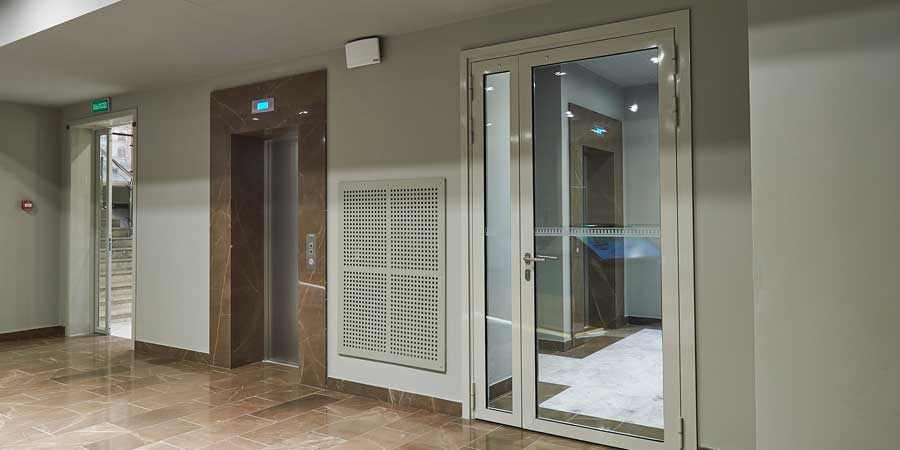
- machine rooms of elevators;
- exits to the attic;
- premises of pumping stations, heating points near industrial and residential buildings, etc.
Where is the PD
That is, where exactly in the above places the fire doors are installed, in general, it is quite simple to determine - the door must be installed in the opening that is available in the fire barrier of the required type.
The types of barriers are determined according to table No. 23, and according to table No. 24 of the Technical Regulations (Federal Law No. 123), we find out which door (what limit of fire resistance) should be placed in a particular room, building / structure.
How to use these tables is discussed below.
First, we must find out what fire barriers are and what function do they perform?
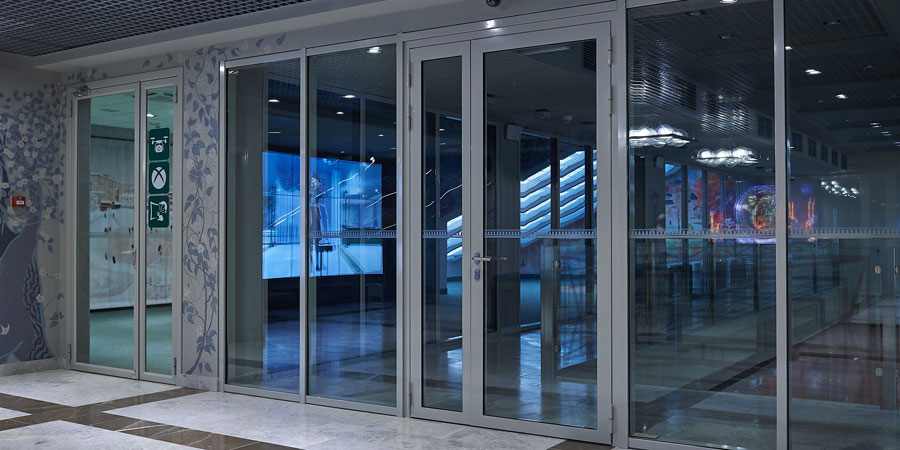
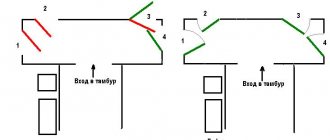
Where are the fire doors installed?
Installation sites are determined by the regulations corresponding to the Code of Rules (SP):
- staircase in a residential building and an office building;
- corridor in industrial premises;
- attic;
- interior doors in archives;
- server room and electrical control room;
- common entrance.
Fire resistance limits of fire doors
The characteristics must comply with GOST, SNiP and SP. The latter are used at the design, construction and reconstruction stages. The fire resistance limits are indicated by EIS, EIW, EIWS, EI, E. Each indicator means a limit of time during which the structure will withstand temperature exposure and prevent the spread of fire and smoke into adjacent rooms.
Fire rating limits indicate how long the door will perform. At the end of the limit, the structure is deformed, the lock may jam. Cracks appear, the sheet (E) may fall out of the box.
The door at the end of the fire resistance limit loses its thermal insulation capacity (I).
Glasses in the structure lose their thermal insulation capacity (W).
To determine the limits of fire resistance, tests are carried out in accordance with GOST.If the structure deforms after 40 minutes of testing and passes smoke after 50 minutes, the limit is 30 minutes (the smallest value is taken).
Manufacturers of fire barriers produce products with fire resistance limits of 30-120 minutes. The maximum limits are from 15 to 360 minutes. After carrying out specialized tests, the structure is assigned the limit established by GOST.
GOST requirements
The standards are developed taking into account the scope of application. Requirements are mandatory for the production and installation of doors. SNiP, GOST and SP - documents regulating control tests. GOST R 53307 2009 provides for fire resistance testing. The length of time in minutes is measured while the door is holding the flame. Another indicator that is obtained as a result of testing is the temperature at which the structure deforms.
SNiP requirements
SNiP 2.01.02-85 regulates the classification of objects, materials and structures according to technical and fire properties. The rules must be taken into account at the design stage of objects for various purposes. The main characteristics of fire doors:
- Flammability level from low to high (G1 - G4).
- Fire hazard from non-hazardous to fire hazardous (K0 - K3).
- Fire resistance limit in minutes (E - appearance of deformation, I - loss of thermal insulation, R - structural integrity).
Example of marking: E-30 will withstand a fire for 30 minutes, E-90 - an hour and a half.
Prototype testing
To obtain the desired readings, a sample of the fire-type door is taken. GOST defines the main results of limiting states.
Loss of integrity (E) occurs when:
- stable flame on an unheated surface for a duration of 10 seconds;
- smoldering, accompanied by the glow of a cotton swab, or ignition under the influence of fire or combustible gases that penetrate through the resulting cracks, cracks, holes, porches;
- slots not less than 150 mm in size, through holes with a diameter of 6 (± 2) mm, probes over 500 mm in length in door samples;
- the prototype falling out of the door frame or the frame itself from the enclosing structure of a standard type.
Loss of thermal insulation properties (I) as a result of:
- an increase in temperature without heating the surface of the prototype by an average of 140 ° C or at any point of the test surface by 180 ° C in comparison with the temperature indicators of the structure before testing;
- increasing the temperature up to 300 ° C on the box of the prototype, regardless of the initial indicator before testing.
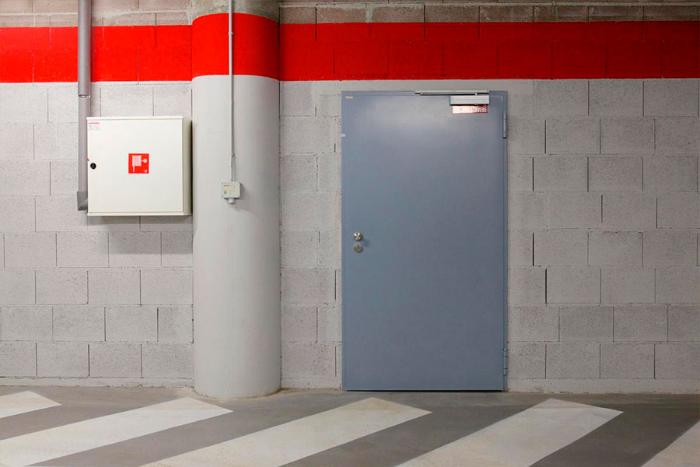
Requirements for premises for the installation of fire doors
Metal barriers will not stop and extinguish the fire, will not become its prevention. Their task is to contain the spread of a dangerous element. Ordinary ones let through flames, smoke, sparks. A fire door will protect the premises from combustion products for a certain time specified in the certificate. According to SNiP of January 21, 1997, structures, sections of various buildings with a certain class of fire hazard must be separated by fire-fighting metal structures.
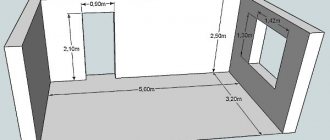
Reference: to install the door, you need an opening from 2 meters in height, from 0.7 meters in width for residential premises. If we are talking about rooms with 15-50 people, then the width of the opening should be from 1.2 meters.
The threshold in the doorway is not prohibited. What cannot be done is to leave mechanisms and structures on the way of evacuation that interfere with the rescue of people. Installation is allowed only by specialists.
Fireproof door material
GOST standards allow several materials that meet all fire resistance requirements. In a large assortment, designs from the following materials prevail today:
- refractory metal - the design on this basis provides reliable protection at critical temperatures;
- fireproof wooden doors. Due to processing with a special composition and coating of MDF canvas, wooden elements can withstand high-quality thermal stress;
- refractory alloys and steel parts make even glass structures resistant to fire.
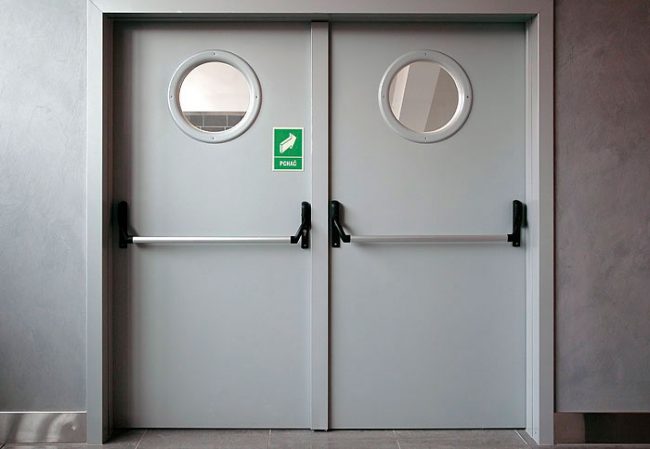

In terms of their design features, fire protection products are similar to conventional entrance doors. The only difference is that refractory elements are modified using special technologies. Such structures are also frost-resistant and sometimes bullet-proof. Therefore, today it is not uncommon for people to install such doors in ordinary apartment buildings.
Before installing the door, you must carefully prepare all the necessary tools and the installation site itself. Further on this will be discussed.


Requirements for a fire door when choosing
The obligation to install a fire door comes from the fire inspector. Fire barriers in the form of gates, hatches, partitions are mounted on objects with a high risk of fire. Depending on the time during which the structure will hold back smoke and fire, different fire resistance is distinguished (EI-30, EI-45, EI-60, EI-90). To select the correct door, taking into account the purpose, they use the norms of the Federal Law.
Order the installation and installation of fire doors and barriers
Test parameters
On the construction market, there is a large selection of fire doors, which are manufactured by different manufacturers.
In accordance with the standards and requirements for fire safety doors, certain parameters are imposed. One standard size is taken for testing, which is reflected in the protocol.
The results obtained apply to products with permissible deviations that vary from + 10% to -30%, both in width and height. In addition, rounding is provided, if upward, then up to 5 cm, downward - up to 10 cm.
The opening and its preparation
In order not to violate SNiP norms when installing the door block, it is necessary to correctly prepare the doorway. The procedure itself does not imply unfamiliar actions, everything is done as in the case of a conventional design. It is necessary to remove the previous box and clean the surfaces.
The adjacent area is also cleaned of foreign objects. When attaching the door, you will have to open it several times to check how correctly it was installed, so foreign objects interfere with this. In addition, they can create an additional source of ignition.
If the fire box is not very reliable, it is reinforced with a special frame. She will also take part of the load.


Preparatory process
Self-installation of a fireproof door: step by step instructions
The thickness of the partition, according to GOST and SNiP, must be at least 12.5 cm. If the wall thickness is less than this indicator, then before direct installation, the indicator must be brought to the appropriate norm. It is worth remembering that the door should open freely to its full width, so it is worth clearing the surrounding area from foreign objects.
Advice. In some cases, it will be necessary to install a reinforcing frame if the wall is not distinguished by its strength.
Next, let's decide on a complete list of tools that will be needed to carry out all the work:
- A drill with a victorious type tip.
- Perforator.
- Hammer, knife, masking tape.
- Polyurethane foam.
- Roulette, level, bolts.
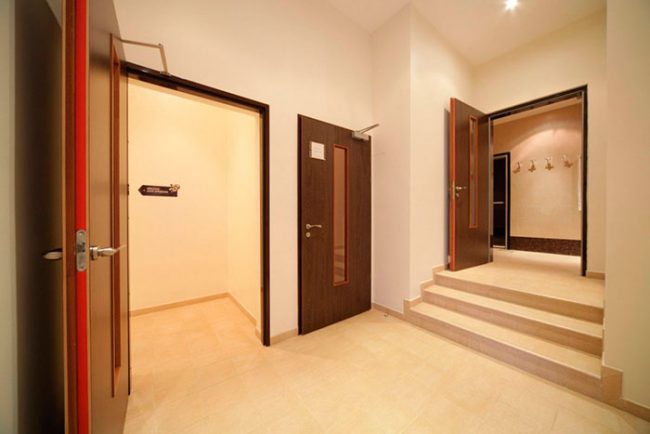


The first step is to assemble the box. All work consists in fastening the corners with screws. Then the door frame is installed in the opening and secured with pegs.The element is aligned using a tape measure and a level. The level of gaps must be observed - they must be the same on all sides. For the anchor bolts, holes are drilled in the wall through the door frame. The door frame is secured with bolts - at least 3 bolts on each side. The joints are filled with a fire-resistant sealant.
The width of the gap between the leaf and the door frame should be within 3 mm, but not more. The canvas itself is installed like a regular front door. There is only one nuance here - the hinges should not interfere with the full opening of the door. Platbands are treated with a special solution, which will give the elements refractory properties. It is best to apply three coats, then let them dry and then install.
After completing the work, make sure that all elements are firmly attached and function correctly. Check the operation of the lock, it should work without interruption. The door itself should open smoothly, without much effort. When opening, there should be no extraneous sounds: squeaks, clicks, taps. If everything is working properly, call the fire inspector, who must make sure that the installation is correct, and enter the result of the check into the protocol with all the necessary signatures and seals.
Article 89 - Fire safety requirements for evacuation routes, evacuation and emergency exits
①. Evacuation routes in buildings, structures and structures and exits from buildings, structures and structures must ensure the safe evacuation of people. The calculation of evacuation routes and exits is made without taking into account the fire extinguishing means used in them.
②. The placement of premises with a mass presence of people, including children and groups of the population with limited mobility, the use of fire hazardous building materials in structural elements of escape routes should be determined in accordance with the requirements of federal laws on the relevant technical regulations.
③. The evacuation exits from buildings, structures and structures include exits that lead:
☞ From the premises on the ground floor to the outside:
➪ directly; ➪ through the corridor; ➪ through the lobby (foyer); ➪ through the staircase; ➪ through the corridor and lobby (foyer); ➪ through the corridor, recreational area and staircase;
☞ From the premises of any floor, except for the first:
➪ directly on the staircase or on the stairs of the 3rd type; ➪ to the corridor leading directly to the staircase or to the stairs of the 3rd type; ➪ to the hall (foyer), which has an exit directly to the staircase or to the stairs of the 3rd type; ➪ to a specially equipped roof section leading to a staircase of the 3rd type;
☞ To an adjacent room (except for premises of class F5, categories A and B), located on the same floor and provided with exits specified in clauses 1 and 2 of this part. Exit from technical premises without permanent workplaces to premises of categories A and B is considered evacuation if equipment for servicing these fire-hazardous premises is located in the technical premises.
④. Evacuation exits from the basement and basement floors should be provided in such a way that they lead directly to the outside and were isolated from the common stairwells of a building, structure, structure, with the exception of cases established by this Federal Law.
⑤. Evacuation exits are also considered:
Exits from the basements through the common staircases into the vestibule with a separate exit to the outside, separated from the rest of the staircase by a deaf fireproof partition of the 1st type, located between the flights from the basement floor to the intermediate landing of the staircases between the first and second floors; Exits from the basement and basement floors with rooms of categories B4, D and D to rooms of categories B4, D and E and the lobby,located on the first floor of F5 class buildings; ☞ Exits from the foyer, dressing rooms, smoking and sanitary rooms located in the basement or basement floors of buildings of classes F2, F3 and F4, to the lobby of the first floor via separate stairs of the 2nd type; ☞Exit from the premises directly to the staircase of the 2nd type, to the corridor or hall (foyer, lobby) leading to such a staircase, subject to the restrictions established by fire safety regulations; ☞ swing doors in gates intended for entry (exit) of railway and road transport.
⑥. Emergency exits in buildings, structures and structures include exits that lead:
☞ on a balcony or loggia with a blank wall at least 1.2 meters from the end of the balcony (loggia) to the window opening (glazed door) or at least 1.6 meters between the glazed openings overlooking the balcony (loggia); ☞ to the passage with a width of at least 0.6 meters, leading to an adjacent section of a building of class F1.3 or to an adjacent fire compartment; ☞to a balcony or loggia equipped with an external staircase connecting the balconies or loggias by floor; ☞ Directly outside from rooms with a clean floor not lower than 4.5 meters and not higher than 5 meters through a window or door measuring at least 0.75 x 1.5 meters, as well as through a hatch measuring at least 0.6 x 0.8 meters. In this case, the exit through the pit must be equipped with a ladder in the pit, and the exit through the hatch - a ladder in the room. The slope of these stairs is not standardized; ☞ on the roof of buildings, structures and structures of I, II and III degrees of fire resistance of classes C0 and C1 through a window or door measuring at least 0.75 x 1.5 meters, as well as through a hatch measuring at least 0.6 x 0.8 meters on a vertical or inclined staircase.
⑧. The number and width of evacuation exits from rooms from floors and from buildings are determined depending on the maximum possible number of people evacuated through them and the maximum permissible distance from the most remote place of possible stay of people (workplace) to the nearest emergency exit.
⑨. Parts of the building of various functional fire hazards are separated by fire barriers and must be provided with independent emergency exits.
⑩. The number of emergency exits from the premises should be set depending on the maximum permissible distance from the most distant point (workplace) to the nearest emergency exit.
⑪. The number of emergency exits from a building, structure and structure must be at least the number of emergency exits from any floor of a building, structure and structure.
Article 90 - Support for the activities of fire departments
⑥. Exits from staircases to the roof or attic should be provided along staircases with platforms before exiting through type 2 fire doors with a size of at least 0.75 × 1.5 meters.