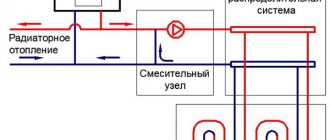
The most common way to provide thermal energy to apartment buildings is central heating. Heating medium supply carried out by means of heating mains from central boiler houses or CHP. The heated liquid is taken over by the heat point... It produces primary heat metering, provides regulation of the supply, distributes it to consumers. There are other options for heating apartments. Among the most common: individual heating of an apartment building, heating of a single apartment.
Each scheme has advantages and disadvantages, the choice of the most convenient one depends on a number of factors: the proximity of the highways, their condition, the expediency of using the energy of remote boilers. In any case, the design of new communications, the reconstruction of old networks should include the development of mechanisms for regulating the supply of heat to apartment buildings. This is not so much a matter of comfort as of saving energy resources.
Automation of the MKD heat supply control
The existing system of transportation and distribution of heat energy is far from ideal. Its imperfection is especially acute during the off-season. It often happens that the weather is stable outside the window, the batteries stubbornly heat the already warm rooms. This situation is due to the fact that the only link in the chain of enterprises, communications and coolant supply devicesthat has the ability to influence the heat supply process is a boiler house or a CHP. But even they do not have the possibility of flexible regulation, they do not have mechanisms that allow them to instantly react to a change in the weather.
Ideal option regulation of heat supply in an apartment building there will be such a project, in the implementation of which it becomes possible to regulate the temperature of each room separately. This solution makes it possible to provide individual metering of heat supply, which in turn makes it possible for residents not to pay for heat that simply flies out through the open vents.
Individual metering of heat supply allows the consumer to carry out regulation of the amount of consumed heat energy... This can be achieved by setting a lower temperature for rooms that are not in use and raising it as needed.
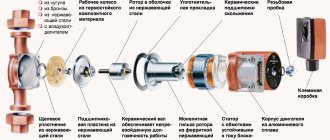
Heat regulation can be realized by shutting off the taps on the radiators. In addition, you can entrust the process of regulation to automation. Modern industry offers various devices that allow you to regulate the room temperature. The most common of these are radiator thermostats. These are devices consisting of a thermostatic head and a valve. The sensor measures the room temperature, controls the valve. Depending on the presettings, the valve increases or decreases the heating medium flow by adjusting the heating level.
Due to the possibility of precise adjustment, this device allows you to regulate the microclimate inside the building, maintain a comfortable atmosphere, and save energy. There are different types of radiator thermostats. Most of them allow you to set the temperature value that the owner of the room wants to receive. There are more complex models.Some of them allow you to set the temperature for different times of the day, for example, they can limit the supply of heat during the day, when there is no one in the apartment, and in the late afternoon they can warm the room to a comfortable level.
Actions in case of non-compliance with heating standards
What to do if the apartment is too cold or too hot? If there is a clear deviation of temperatures from the optimal temperature regime, the tenant can, independently or together with neighbors, invite the employees of the management company to take measurements. The management company must respond to every request from residents, taking measurements on demand.
If the appeal to the management company did not produce the desired effect and did not lead to an improvement in the situation, the consumer should file complaints with the local authorities of the housing inspection and Rospotrebnadzor. The last step in the fight for comfortable living conditions is going to court with a claim against the management company.
It is important to know: Act of hydraulic testing of the heating system
Heat regulation in individual heating systems
The concept of individual heat supply means that the boiler room is located directly in an apartment building. For its placement, basements, basements are used, modular boiler rooms are also used, which are placed on the roofs of buildings.
The implementation of individual heating in apartment buildings is a rather expensive project. It requires a significant investment, however, it provides an opportunity to save money. Length of mains for individual heat supply limited by the size of the building, which entails small heat losses during transportation. In addition, easy access to the boiler room equipment makes it possible to more efficiently regulate the heat supply to the apartment building.
A separate case of individual heat supply is the installation of autonomous heating in the apartments of an apartment building. For this, boilers are used, most often gas ones, which are part of a closed heating system. Such a solution makes it easy to automate the process by using devices that can regulate the temperature of a single room.
Flushing of central heating systems of apartment buildings OZP 2011-2012.
When preparing the multi-apartment housing stock for the autumn-winter heating season, one of the points provides for flushing and pressure testing of central heating systems in multi-apartment buildings. The rules and norms for the technical operation of the housing stock approved by the decree of the State Construction Committee of the Russian Federation of September 27, 2003 No. 170 determine the flushing of the central heating system of an apartment building (hereinafter MKD): clause 9.2.9. Flushing of systems is carried out annually after the end of the heating period, as well as after installation, overhaul, maintenance with replacement of pipes (in open systems, systems must also be disinfected before commissioning). The systems are flushed with water in quantities exceeding the design flow rate of the heat carrier by 3 - 5 times, while complete clarification of the water should be achieved. When carrying out hydropneumatic flushing, the flow rate of the air mixture should not exceed 3 - 5 times the design flow rate of the coolant. For flushing, tap or industrial water is used. Connecting systems that have not been flushed is not allowed. Flushing the heating system ensures better circulation of the coolant and heat transfer, and as a result, less energy consumption, which leads to comfortable living during the heating season and savings in payment for this type of service. To carry out the measures, you need to submit an application for flushing the heating system of the MKD to the district heating organization as soon as possible.It should be recalled that the owners of residential premises of apartment buildings, in accordance with Article 161 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation of December 29, 2004 No. 188-FZ, must choose and implement a method of managing an apartment building. The implementation of the selected management method provides for the conclusion of contracts for the supply of energy resources and maintenance, by specialized organizations, of the building's public utility networks of an apartment building. If the owners of residential premises of MKD do not comply with the above legislative requirements, then local authorities in the manner prescribed by the Government of the Russian Federation recognize the selected management method as not implemented and conduct an open tender for the selection of a managing organization in accordance with the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of 06.02.2007 No. 75 "On the procedure for holding an open tender by the local government body for the selection of a management organization for the management of an apartment building ”, that is, the management organization will deal with the management of the apartment building.
Administration of the Municipal Formation Korenovsky District 07/22/2011
Explanation: Appendix to the letter to the administration of the Korenovskiy district
MINISTRY OF ENERGY OF THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION
ORDER of March 24, 2003 N 115
ON APPROVAL OF THE RULES OF TECHNICAL OPERATION OF THERMAL POWER PLANTS
9.2. Heating, ventilation, air conditioning, hot water supply systems
9.2.1. The deviation of the average daily temperature of water supplied to the heating, ventilation, air conditioning and hot water supply systems must be within +/- 3% of the established temperature schedule. The average daily temperature of the return water supply should not exceed the temperature set by the temperature schedule by more than 5%. 9.2.2. During the operation of heating, ventilation and hot water supply systems, the hourly leakage of the coolant should not exceed the norm, which is 0.25% of the volume of water in the systems, taking into account the volume of water in the distribution heat pipelines of the systems. When determining the rate of leakage of the coolant, the water consumption for filling the heat consumption systems during their scheduled repair is not taken into account. 9.2.3. In systems, hot water is usually used as a heat carrier. Other coolants are allowed to be used for a feasibility study. 9.2.4. All the upper points of the distribution pipelines are equipped with air outlet fittings, and the lower ones - with fittings for draining water or draining condensate. 9.2.5. The pipelines are made with slopes to exclude the formation of air pockets and the accumulation of condensate. 9.2.6. The nodal points of the in-house heat pipelines are equipped with sectional valves (valves) to disconnect individual sections from the system. 9.2.7. As a source of thermal energy for systems, the secondary heat of technological power plants should be used as much as possible. 9.2.8. The use of electricity for heat supply purposes is allowed to be used in a feasibility study. 9.2.9. Flushing of systems is carried out annually after the end of the heating period, as well as after installation, overhaul, routine repairs with replacement of pipes (in open systems, systems must also be disinfected before commissioning). The systems are flushed with water in quantities exceeding the design flow rate of the heating agent by 3 - 5 times, annually after the heating period, while complete clarification of the water is achieved. When carrying out hydropneumatic flushing, the flow rate of the water-air mixture should not exceed 3 - 5 times the design flow rate of the coolant. To flush the systems, tap or industrial water is used.In open heat supply systems, the final flushing after disinfection is carried out with water that meets the requirements of the current standard for drinking water, until the indicators of the discharged water reach those required by sanitary standards for drinking water; for condensate pipelines, the quality of the discharged water must meet the requirements depending on the scheme for using condensate. Disinfection of heat consumption systems is carried out in accordance with the requirements established by sanitary norms and rules. 9.2.10. Connecting systems that have not been flushed, and in open systems - flushed and disinfected, is not allowed.
Appendix to the letter to the administration of the Korenovskiy district
STATE COMMITTEE OF THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION FOR CONSTRUCTION AND HOUSING AND UTILITIES
REGULATION of September 27, 2003 N 170
ON THE APPROVAL OF THE RULES AND STANDARDS FOR TECHNICAL OPERATION OF THE HOUSING FUND
5.2.10. Flushing of heat consumption systems is carried out annually after the end of the heating period, as well as installation, overhaul, routine repairs with replacement of pipes (in open systems, systems must also be disinfected before commissioning). The systems are flushed with water in quantities exceeding the design flow rate of the coolant by 3 - 5 times, while complete clarification of the water should be achieved. When carrying out hydropneumatic flushing, the flow rate of the air mixture should not exceed 3 - 5 times the design flow rate of the coolant. For flushing, tap or industrial water is used. Connecting systems that have not been flushed, and in open systems, flushing and disinfection is not allowed.
Single-pipe version of MKD heat supply
The simplest option for heating an apartment building is a one-pipe system. The heat carrier is fed from the bottom up, it fills the radiators, gives off heat and moves to the next consumer. This system has a number of significant disadvantages. One of the main ones is significant heat loss during transportation. The last consumers in the chain receive a slightly heated liquid.
In addition, the one-pipe system makes it almost impossible to regulate the heat supply in an apartment building. It is impossible to install taps or automatic control devices on the supply pipelines, since a decrease in the flow rate inside any of them will affect the entire system. You also need to remember about possible emergency situations. A one-pipe system does not allow one of its components to be replaced without completely draining the water from the system. A minor breakdown may result in stopping the supply of heat to all consumers.
Heat supply and regulation in a two-pipe system
This option is more complicated, but it allows you to significantly expand the capabilities of the mechanisms regulation of heat supply to each consumer... The difference between the system is that the coolant that has given up part of the energy does not continue to move along the same pipe to the next consumer, it flows into the second pipe, the "return". Due to this, the coolant has approximately the same temperature all the way, for each radiator.
It is this solution that makes it possible to carry out regulation of heat supply in an apartment buildingusing each individual radiator. The temperature can be controlled either manually, with a valve, or automatically, using thermostats.
Regardless of how the heat supply is implemented, the system must include devices for automatic metering and regulation of heat supply in an apartment building. This allows not only to provide housing with the heat necessary for life, but also to significantly save energy resources.
Heating standards in a residential building
It is not necessary for a consumer of thermal energy, that is, a home owner or a person who permanently resides in this house, to know all the subtleties of regulatory documentation and the rules for organizing a heating system. But everyone needs to have an idea of what thermal regime the heating system of a residential building should provide. Here are the basic requirements and rules that apply to residential and utility rooms:
- In living rooms, the temperature should be within + 20- + 22 degrees. A short-term deviation up or down is allowed, however, fluctuations of more than 2 degrees are not allowed.
- In the kitchen and toilet, the temperature should be 1 degree lower than in the living rooms. It is allowed to increase up to +26 degrees, this is due to the work in the kitchen of a gas stove or other heating devices. But the maximum allowable temperature drop is the same as in residential premises.
- In the bathroom, the temperature level should be higher and be within + 24- + 26 degrees.
- In corridors and on staircases, where a person goes in warm clothes, the temperature should be within + 16- + 18 degrees.
It is important to know: VAT exemption for housing and communal services management companies
Additional Information
As practice shows, it is the temperature regime of staircases and spans that is the worst observed - this is due to high heat losses. However, such a violation will certainly lead to a cold snap in the apartment, so residents have the right to file a complaint with the Criminal Code.