Plastic windows are installed both in multi-storey buildings and in wooden houses. They are deservedly popular, as they have many advantages over wooden frames.
Benefits:
- durable,
- durable,
- aesthetic,
- environmentally friendly,
- functional,
- are not blown
- do not take up a lot of space in the window opening, which allows you to increase the window sill.
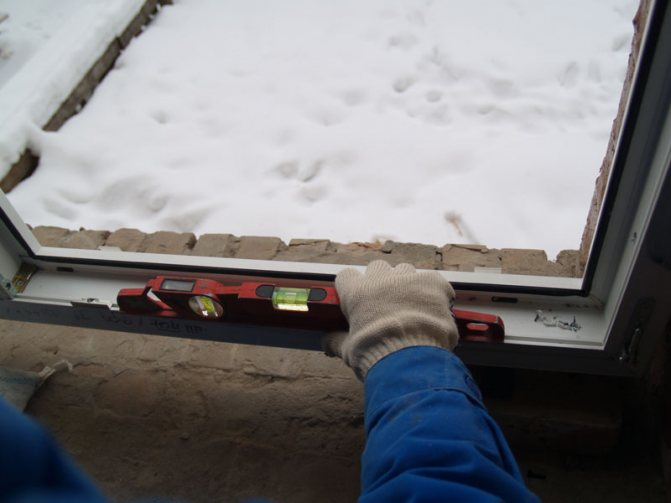
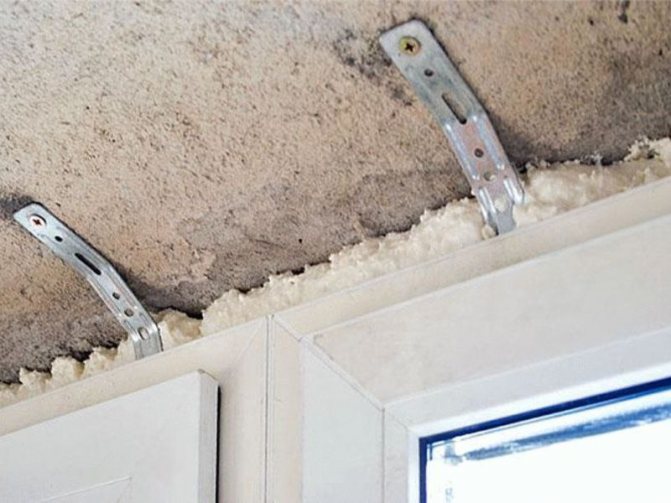
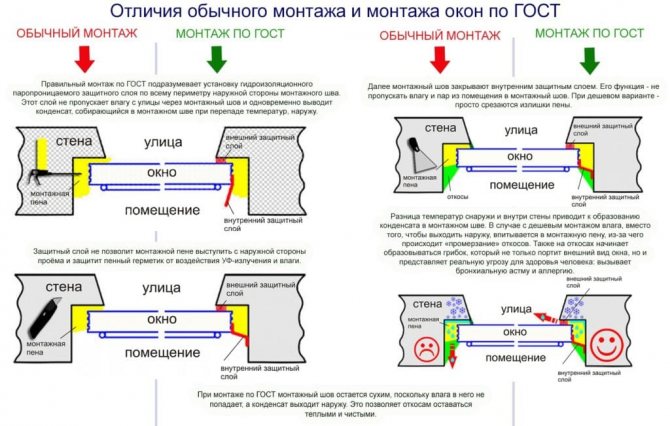
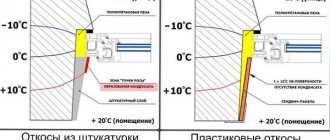
However, some advantages, for example, durability and tightness, are achieved only if the windows are installed in accordance with GOST. Not all installers follow these rules. This does not mean that the window block will fall out of the window opening. However, after the change of seasons of the year, gaps may appear, which will become cold bridges. The window can be skewed in the opening, which will cause problems with closing and opening the sashes.
Installation seam requirements
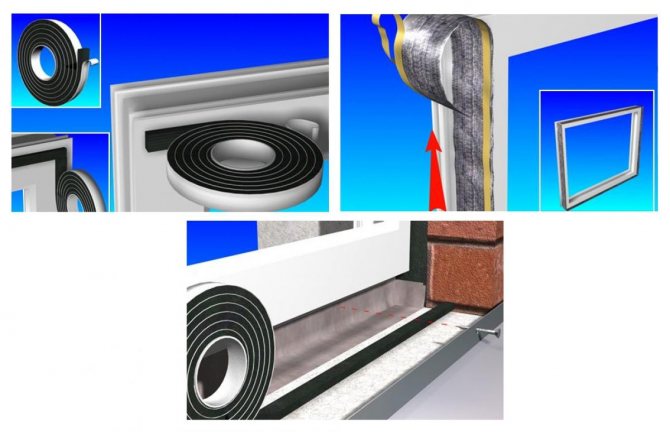
The quality of the installation seam laying is of great importance during installation. It is he who provides tightness and protection from moisture. The assembly seam in accordance with the current GOST 30971-2012 must:
- consist of at least three layers;
- be sealed;
- be denser on the inside than on the outside;
- be made of those materials, the service life of which is comparable to the estimated service life of the window - at least 20 years of conditional operation.
Window block installation diagram
Basic standards
Compliance of windows with GOST is a very important fact in the construction of residential and public buildings. All state standards were developed in order to carry out any production processes, in accordance with the accepted and proven technological activities.
GOST maintains the safety of work, ensures the reliability and strength of the structure to be installed. According to the developed state standards, each stage of work on the installation of window joint ventures is carried out: from the choice of the type of mounted unit to the requirements according to which the surface preparation is carried out, where the installation will be performed.
The sanitary and epidemiological rules and regulations of SanPiN 2.1.2.2645-10 include the following standards for living conditions in a residential building or premises:
- the movement of ventilation in a residential building is carried out by an inflow of air, which enters a window, a transom or a corresponding opening that has window sashes and a ventilation system. Exhaust ducts must be carried out in the kitchen, bathroom, bathroom and drying chamber;
- the degree of noise effects created by external factors in the dwelling is taken into account, according to the measurements, when the window sash, transom or window leaf is open.
Insulation materials used for window installation
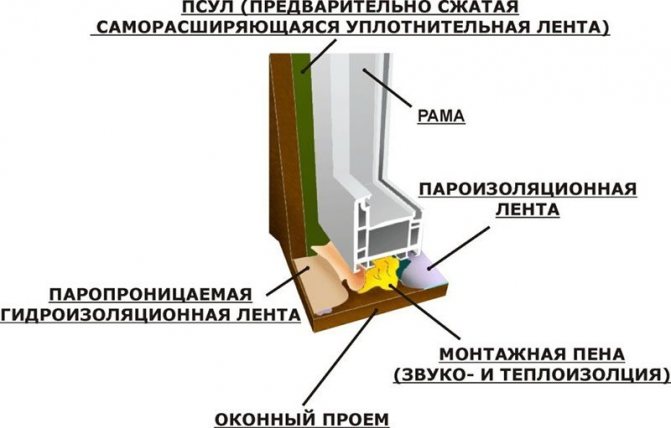
The functions of the joint layers are different. They are designed to provide steam, sound and heat insulation:
- The main one provides sound and heat insulation.
- External - protects the seam from atmospheric moisture penetration.
- Internal - protects against steam coming from the room.
- Additional (arranged in concrete and brick buildings) - protects against moisture absorption from the wall material by the seam material.
Seam layers perform different functions
Therefore, different types of vapor barrier tapes are used in different areas:
- PSUL - is installed to seal external joints. It has a self-expanding ability, and therefore fits tightly to surfaces.
- ВС (ВС +) - used for vapor barrier of internal slopes, installed dry, meaning drywall or plastic.
- VM (VM +) - used for finishing interior slopes, which will subsequently be covered with plaster.
- GPL (GPL +) is a universal tape capable of performing the functions of steam, sound and noise insulation. It is made on the basis of polyethylene foam, on one side it is laminated with a polyurethane film.
Outside, membrane-type waterproofing tapes are also used, which serve to drain precipitation.
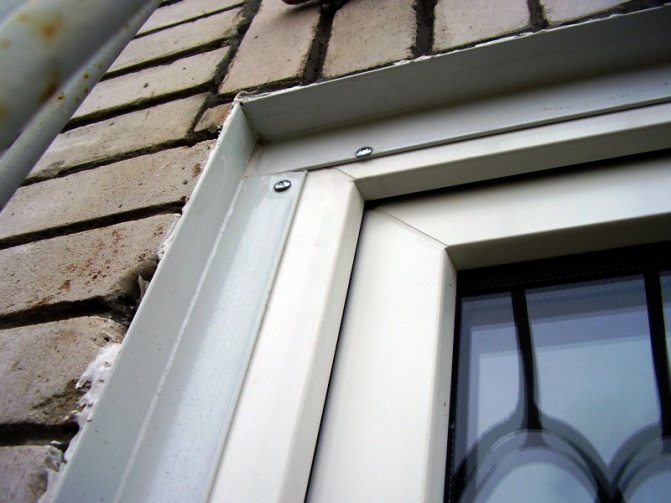
To improve performance, additional weather protection elements can be used. For example, strips and linings, as well as an ebb installed from the bottom of the window.
From the inside, the seam is plastered or slopes and a window sill are installed.
Construction of plastic windows
The content of the article
1 Construction of plastic windows 1.1 Structure of a window 2 How to measure a plastic window 3 Preparation 4 How to install correctly: choosing an installation method 5 Installing plastic windows with your own hands: step-by-step instructions 5.1 Installation with unpacking 5.2 Installation without unpacking
To properly understand the installation process, you need to have an understanding of the construction of windows. Let's start with materials and titles. Plastic windows are made of polyvinyl chloride, which is abbreviated as PVC. Hence the second name - PVC windows.
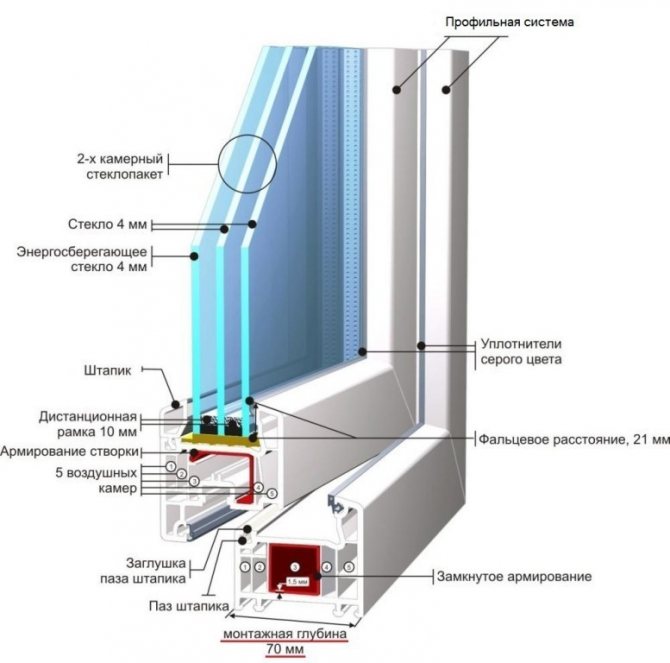
The main element of any window is the frame. For plastic windows, the frame is made of a special multi-chamber profile. It is divided by partitions into a number of cells - chambers. The more of these cells, the warmer the window will be. When they talk about how many cameras there will be in a plastic window, they have the number of cells in the profile.
Windows from the same manufacturer with a different number of cameras in the profile
In the middle of the structure, in the largest chamber, a blue insert is visible. This is a reinforcing element of increased rigidity. It gives the profile the required strength. In plastic windows this insert is made of plastic, in metal-plastic windows it is made of metal (usually it is made of aluminum). That's the whole difference between them.
The structure of a metal-plastic window
There is also a division of profiles into classes: economy, standard and premium. The best choice if you need normal windows is the standard class. In the economy class, partitions are too thin and they begin to freeze almost from the moment of installation. The premium has a high price tag due to options that, in fact, are not needed.
If you want to have the best profile for plastic windows, take the class standard of any factory. There is no particular difference between the products of different companies. They have been standardized for a long time and all the stories of managers about the benefits are fairy tales. If they are made on factory equipment, there is no difference between them: all factory profiles have been standardized for a long time.
Window profiles are white as standard, but they can also be brown - to match the color of any tree, and even pink - on request. Colored profile windows are more expensive than similar white ones.
Window structure
To understand what is at stake in the description of the installation process, you need to know what each component of the structure is called.
What does a plastic window consist of?
It consists of:
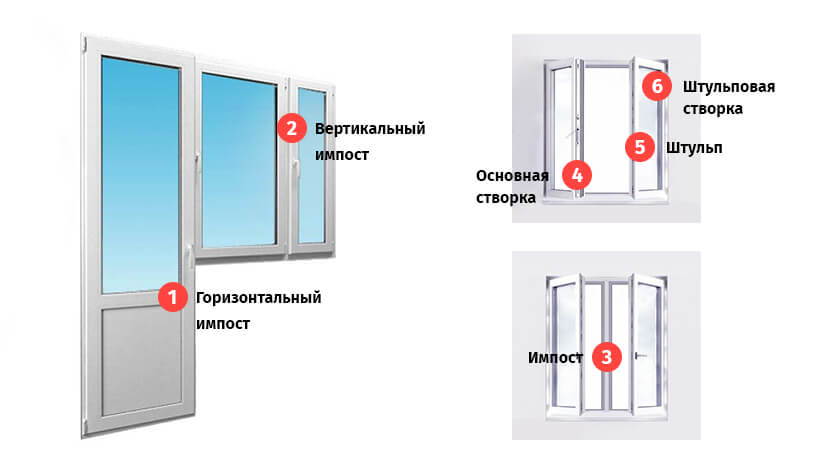
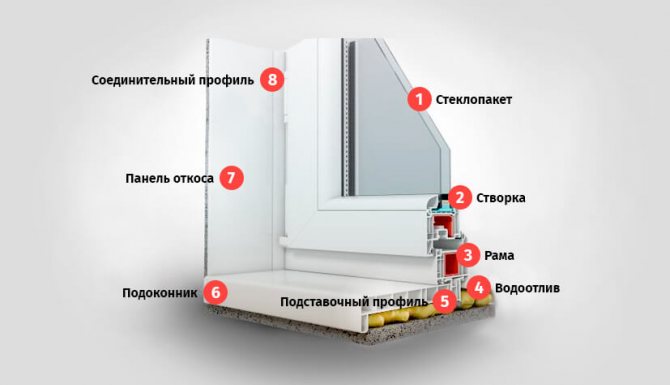
Frames. This is the base of the window. If the window consists of several parts, the frame is divided into parts by an impost - a vertical component. If the window is of two parts, there is one impost, If of three - two, etc. The opening part of the window is called a sash, the fixed part is called a capercaillie. A double-glazed window is inserted into them - two, three or more glasses, hermetically fastened together. A foil tape is laid between the glasses, which ensures tightness. There are double-glazed windows with special properties: with reinforced glass, tinted and energy efficient, which, according to manufacturers, reduces heat loss through windows. There are also double-glazed windows, between the glasses of which an inert gas is pumped. It also reduces heat loss.Double-glazed windows are pressed against the frame with a cap - a thin plastic strip. The tightness of the connection is ensured by a rubber seal (it is usually black). Locking fittings are installed on the sashes. This is a specific set of mechanisms that provide opening and closing. They can be different, as they provide different functionality: opening, opening with ventilation, opening + ventilation + micro ventilation. To ensure tightness on all parts - frame, impost and sashes - rubber seals are installed.
At the bottom on the outside of the frame (the one that faces the street) there are drainage holes that are covered with special caps. Through them, condensation is discharged into the street, which forms inside due to the temperature difference between the street and the room.
Drainage holes
The window also has an ebb - a board outside that removes precipitation and a window sill inside. The side and upper parts from the street side and the premises are sealed with slopes. They can also be made of plastic or made using a different technology.
Read how to adjust the PVC window here.
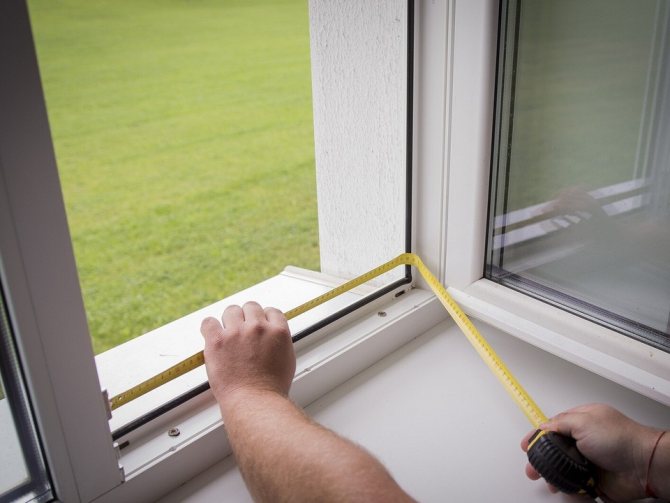
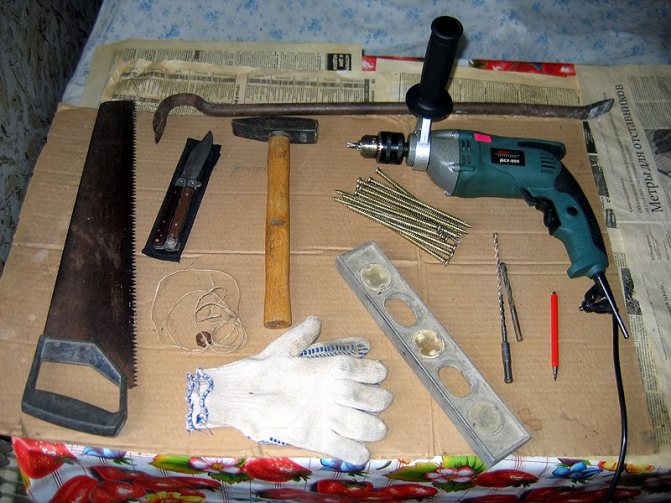
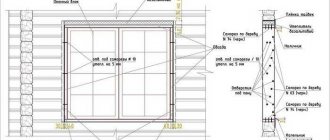
Preparation of a window opening
Before carrying out work, a workplace is prepared. All furniture is removed from the window, curtains are removed. Using a puncher, a saw removes the old window block.
During the dismantling of the old unit and the installation of a new one, fine dust is formed, which will settle on the floor next to the window and on the furniture in the room.
Plaster is removed from the window opening. If there are sinks or overlays larger than 10 mm, they must be repaired. Relatively small sinks are putty with waterproof putty, larger voids are sealed with plaster, rigid insulating materials or wood treated with antiseptics. When using mineral wool, they provide moisture protection.
Only those surfaces that will directly affect the quality of the window installation are treated with plaster: this is part of a quarter of the window opening with a width of about 25 mm, a section of the surface of the inner wall slope, i.e. directly those surfaces with which the vapor barrier tape will come into contact.
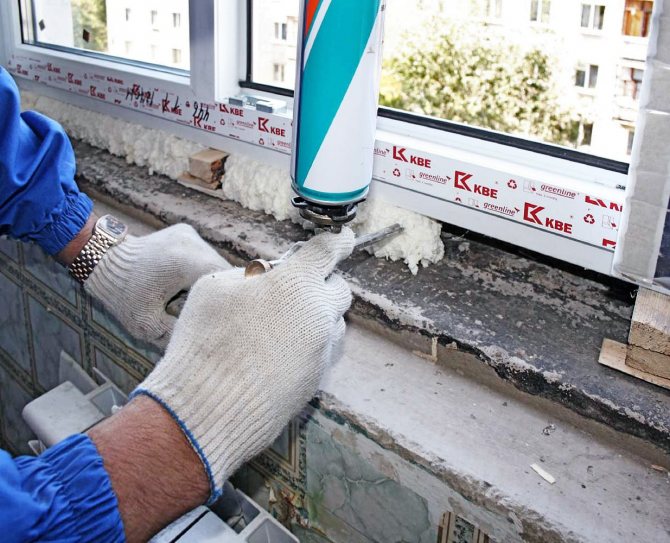
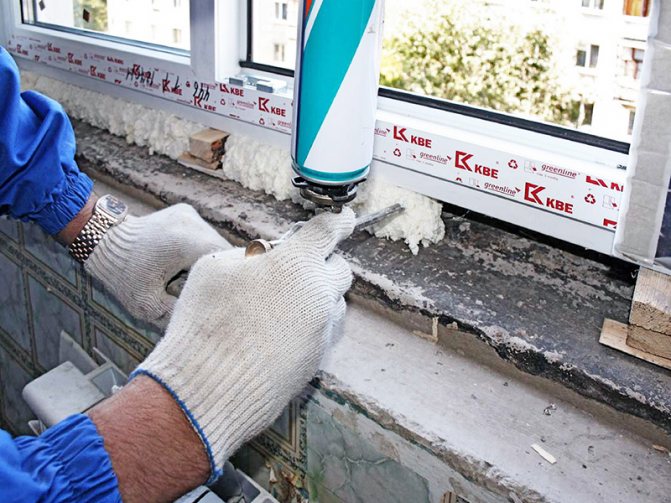
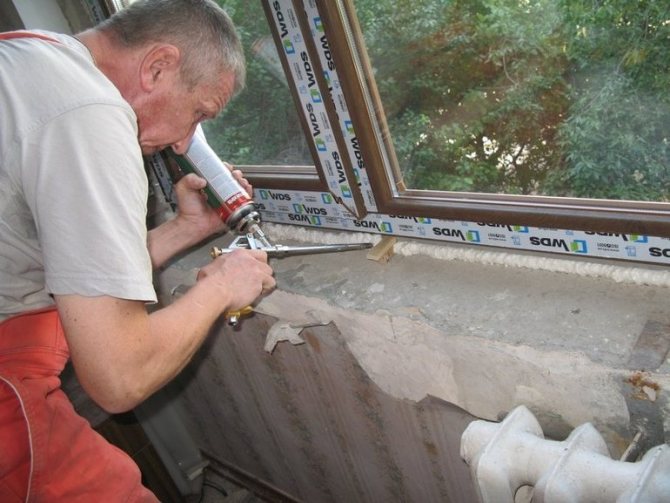
Sealants
Silicone, acrylic or polysulfide liquid mastics are now mainly used to insulate the seam from the outside and inside.
- Silicone. This type of sealant is currently the most popular and frequently used for installation. There are two types of silicone insulators: neutral and acetate.

The latter adhere well only to smooth surfaces (glass, plastic, painted wood, etc.), therefore, they are practically not used to isolate joints in stone buildings. As for the neutral ones, they adhere perfectly to both the PVC profile and the hardened cement mortar. Both materials are easy to use, non-toxic and capable of maintaining performance over a wide temperature range (-50 to + 170). - Acrylic. Compared to silicone counterparts, it is much stronger and more durable, in addition, the variety of textures and colors of acrylic is better combined with most materials used for finishing the facade of the building.


Acrylic waterproofing mastics, unlike silicone mastics, are less elastic, therefore their use is not recommended in buildings with possible shrinkage, for example, in wooden log cabins or frame houses. - Polysulfide (thiokol). This type of waterproofing is similar in its characteristics to neutral-based silicone putties.


In consistency, it is a low density, viscous mixture. For better adhesion to concrete or stone, it is advisable to pre-treat the surface with a special primer.The material has high waterproofing performance and can be used in any climatic conditions.
Unlike film materials, sealants practically do not allow moisture to pass through, which may be in the inner part of the seam, which must be taken into account when used for insulation outside the premises.
There are also specialized developments, for example, the SASI installation system is widespread from those available on the domestic market. This installation method fully complies with GOST standards and involves the use of two types of sealant. For outdoor use, a vapor-permeable one-component waterproofing has been developed STIZ-A, and for indoor processing, acrylic vapor barrier mastic STIZ-V is used.
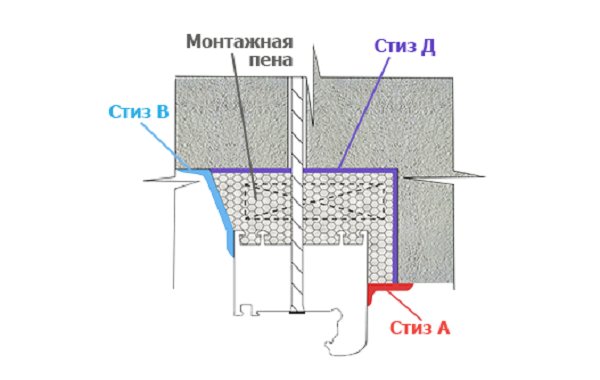

The use of sealants Stiz A, V, D in combination with the installation of windows
Scope of the document
Until 2014, the requirements of 2002 were in force in Russia, which were almost immediately recognized as obsolete due to the rapid development of the specialized industry. In 2012, an interstate standard was developed - GOST for PVC windows 30971−2012. It was accepted by an international commission. On January 1, 2014, the document came into force in Russia as a national standard. It's important to know:


- The document emphasizes that it was developed on the basis of many years of experience, analysis of the use of blocks in different natural conditions, climatic zones in the Russian Federation and the CIS countries. The act should ensure an increase in the comfort of housing, the durability of structures and the overall energy efficiency of the construction sector. It is required for specialized organizations of any form of ownership.
- The document is intended for practical use when working with gaps between the main wall opening and a block-window frame. It is also necessary to focus on it at the stage of design and installation of adjacent units of windows, doors (including balcony), gates, tape structures, stained-glass windows.
- The standard must also be observed when preparing design and technological documents for the construction or reconstruction of housing.
- The Act does not apply to suspended structures, transparent roofs, winter gardens, mansard blocks, as well as special structures with additional safety requirements.
Amendments and changes that are made to the document are published in the journal "National Standards". They can also be found on the Rosstandart website, where the data is updated in operational mode. Here, you can download the acts, and not focus on paid resources with outdated information and a lot of unnecessary advertising.
Quality assessment, control methods, guarantees
When accepting completed works (6), the following stages of control are distinguished:
- incoming - upon receipt of raw materials;
- preparation of openings and blocks;
- meeting the general requirements for installation;
- operating;
- acceptance;
- laboratory with tests.
Test methods (7) are to determine empirically:
- Strength and adhesion of insulation foam.
- Deformation stability.
- Sizes and quantities of samples.
The presentation of the results is highlighted in a separate subsection.