Balcony slabs are designed for residential buildings and general-purpose buildings of certain type series. They are a solid structure used to equip balconies and loggias, they are attached to the building, taking into account the protrusion beyond the wall. For the convenience of loading and installing the plates, they have metal hinges, which are then welded to the iron rods.
Slabs can have different shapes, and they are all made using monolith technology, which can significantly increase the strength of the structure. In factories, as a rule, rectangular plates are made, as required by GOST. Usually, the plates are chosen depending on the following factors:
- Requirements for the construction of a structure
- Structural system of each building
- Features of urban planning
- Task type for builders and architects
SNiPs and GOSTs of balconies and loggias - construction documentation
Having decided to re-equip or repair a balcony or loggia in your apartment, you should understand that any manipulations associated with the reconstruction and redevelopment of these premises must necessarily comply with regulatory requirements. The main document regulating this kind of activity is SNiP. Balconies and loggias, in accordance with this set of rules, are designed and built taking into account in order to prevent their damage and destruction during operation.
According to the requirement of SNiP, a loggia or balcony of an open or closed type should not exert additional pressure on the supporting and enclosing structures of the building in which they are located. When installing them, it is also important to take into account fire safety requirements and established sanitary standards.
In addition, this normative act explains in which cases the construction of these premises is impractical due to the unfavorable conditions of their operation. GOST loggias and balconies are taken into account in the documentation SNiP 31-01-2003 "Multi-apartment residential buildings", which contains a detailed list of conditions that must be met when redeveloping and refurbishing these premises, as well as general requirements for the construction of residential buildings of various types.
SNiP 31-01-2003 "Residential apartment buildings" (406 KB, pdf)
One of the important stages associated with the arrangement of balconies and loggias of various types is the construction of a new balcony fence, which ensures reliable and durable fixation of the main structure. When performing work of this type, you should use GOST balconies fencing, number 25772-83, containing instructions on the design and installation of fences of various types.
In accordance with the established standards, only screen-type structures can be used for fencing balconies and loggias. Moreover, these elements must withstand the level of loads provided for in SNiP 2.01.07. GOST for balconies indicates that the total height of the balcony railing should be:
- in buildings up to 30 m high - 1000 mm;
- above 30 m - 1100 mm.
In this case, the height of the railings of the enclosing element should be at least 900 mm, and their bearing capacity should be an order of magnitude higher than the usual stair railings. One of the important conditions for their design and construction is the absence of sharp protrusions and rough edges.
Also, increased requirements are imposed on the safety of the balcony railings being erected. For this purpose, the use of horizontal elements is prohibited on them.
GOST 25772-83 Steel railings for stairs, balconies and roofs. General specifications (449 KB, pdf)
The most common technique used to ensure a sufficient level of noise and heat insulation on balconies and loggias of various types is their glazing. The basic requirements for devices for window and balcony door blocks are described in GOST 30777-2012.
This set of rules contains instructions for the manufacture and installation of swivel, tilt and swing-out devices, as well as other elements included in the package of window and door balcony blocks of various types.
In particular, it contains technical requirements for the design, dimensions and maximum deviations, reliability and resistance to loads and ergonomic performance of structures made of various materials used for glazing balconies.
In addition, this document also contains annexes with diagrams and examples of the device of pivoting, folding and swing-out mechanisms with separate assemblies and elements.
GOST 30777-2012 Devices rotary, folding and swing-out for window and balcony door blocks. Specifications (2.2 MB, pdf)
The rules for glazing balconies in accordance with GOST are described in the document “Assembly window seams with vapor-permeable self-expanding tapes. Specifications "(GOST R 52749-2007). It specifies the requirements for the installation of assembly seams during construction work when installing window and door blocks.
GOST R 52749-2007 Assembly window seams with vapor-permeable self-expanding tapes. Specifications (1.09 MB, pdf)
The basis of any balcony structure is a reinforced concrete slab, on which the remaining elements of the structural system of this building element are fixed. For this purpose, flat hollow-core, flat solid and ribbed loggia slabs are used. GOST 25697-83 “Reinforced concrete slabs of balconies and loggias. General technical conditions ”subdivides them into varieties of cantilever and beam types, differing in the way of arrangement in relation to the supporting structure and the peculiarities of the operation of the slab.
At the same time, the choice of the shape and size of the slab in each case is made in accordance with the construction conditions, structural features of buildings and architectural and artistic tasks.
GOST contains technical requirements for the manufacture and installation of these elements, indicating the maximum permissible deviations, as well as quality standards and the appearance of products. It also contains background information related to the peculiarities of the operation of balcony slabs and the grades of concrete used for their manufacture.
SNiP 31-01-2003 "Residential apartment buildings" (406 KB, pdf)
The document was updated in 2021 and now looks like JV 54.13330. It is related to buildings, the height of which does not exceed 75 m. The list of requirements and standards has two goals: to increase the level of safety of people and to preserve buildings. The information is accompanied by a listing of GOSTs, which must also be observed in the process of construction or reconstruction.
The text of the section reveals the terminology, contains references to sanitary standards (SanPiN) and other related standards. Separately, the dimensions of stairs, doorways, elevators are discussed regarding the transportation of bedridden patients or the movement of disabled people in wheelchairs. The dimensions of the apartments are affected, the conditions necessary for the design of balconies are listed.
All SNiPs and GOSTs concerning balconies and loggias - technical documentation for builders
When redeveloping / reconstructing balconies and loggias, all manipulations must be carried out taking into account regulatory requirements. SNiP is the main document regulating such activities. It is a collection of building codes and regulations.In accordance with this document, at the stages of design and construction of balconies and loggias, the likelihood of their damage and destruction during operation should be excluded.
In accordance with the requirements of SNiP, the loggia and the balcony, regardless of their type (open, closed), should not additionally load the supporting and enclosing structures of the building in which they are being erected. During their construction, it is imperative to take into account the fire safety requirements, to carry out all actions in accordance with the established sanitary standards. When there are unfavorable operating conditions for loggias and balconies, their arrangement is impossible. The SNiP also indicates in which cases the construction of such premises is not carried out.
Documentation SNiP 31-01-2003 "Residential apartment buildings" was compiled taking into account the requirements of GOST for loggias and balconies. Here you can find a detailed list of conditions that cannot be neglected when converting and redeveloping these premises, and general requirements for the construction of various residential buildings.
The creation of a balcony railing is one of the most important stages in the arrangement of loggias and balconies. Durability and reliability of the main structure depend on the quality of the work performed. In their implementation, GOST 25772-83 is used. The established norms are allowed to use only one type of structure - screen-type fences. In this case, the elements used must necessarily withstand the loads specified in SNiP 2.01.07.
In accordance with GOST balcony railings, their total height depends on the height of the building and should not exceed 1000 mm at its values less than 30 m, 1100 mm at a height of more than 30 m. The minimum permissible height of the railing is 900 mm. Railings must have a higher load-bearing capacity than stair railings. In order to ensure a high level of safety, it is forbidden to use elements of the horizontal type, as well as products with raw edges and sharp projections.
Heat and sound insulation of balconies and loggias are created using glazing. The basic requirements for devices intended for door and window units are specified in GOST 30777-2012. It contains the rules in which we are talking about the manufacture and installation of folding, swivel, swing-out products, and other elements presented in a complete set of different door and window blocks. In addition, this document contains applications that allow you to familiarize yourself with installation diagrams and examples of devices for folding, swiveling, swing-out mechanisms with individual units and elements.
In the process of glazing balconies, it is necessary to comply with GOST R 52749-2007. This document contains all the requirements that should be adhered to when creating assembly joints during construction work in order to install door and window blocks.
Balcony structures are always made on the basis of a reinforced concrete slab to which other elements are attached. It is possible to use ribbed slabs, flat solid slabs or hollow-core slabs.
In GOST 25697-83, reinforced concrete slabs are divided into varieties of beam and cantilever type. The differences include the method of location in relation to the supporting structure and the features of their operation. The shape and size of the products are selected depending on the construction conditions, architectural and artistic tasks, and the structural features of the building.
Required set of documents
In accordance with the new national standard (clause 7.4), the manufacturer of translucent products must present the following documents when delivering them to the facility:
- product passport (GOST 23166, 30674, 31462);
- executive, or summary design specification;
- test reports (in accordance with table 4 of GOST R 56926-2016);
- technical documentation confirming the compliance of structures with the requirements of the project;
- if a contract is concluded not only for manufacturing, but also for installation, - a project for the production of installation work (according to GOST 30971).
The difference between a balcony and a loggia
Modern building technologies and layout options have erased some of the signs between the balcony and the loggia - essentially different types of structures. It is important to see the difference between them when calculating the usable area - during the registration of housing transactions, repairs, redevelopments, finishing work.
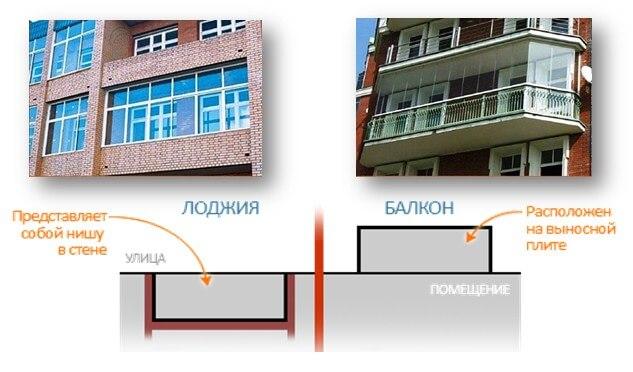
A balcony is a room that is attached to the wall of a building in different ways and protrudes beyond the boundaries of its facade. The outer perimeter has fences.
A loggia is an extension that is part of a building with one, two or three open sides, based on an element of the supporting structure. The facade can be decorated with a parapet, arcade, colonnade.
On a note. It is not difficult to visually distinguish a balcony from a loggia. The balcony goes beyond the perimeter of the house, and the loggia is buried in it.
These two designs also differ in shape. Since the loggia exactly repeats the outline of the building, it can have only two shapes - angular or rectangular.
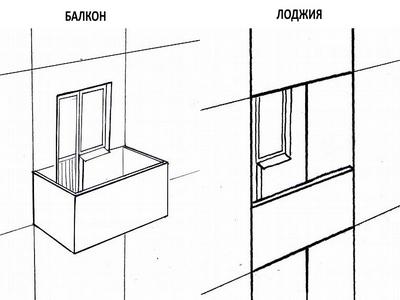

The standard types are generally rectangular. In houses built according to individual projects, there may be balcony structures of the following types:
- Rounded;
- Arrow-shaped;
- Triangular;
- Beveled;
- Elongated.
Other distinguishing features of these two designs include the following:
- The design of the balcony protrudes beyond the facade, the loggia does not.
- The balcony with the building has one common wall, the loggia has three. There are two common walls in the corner and semicircular loggias.
- The loggias, in contrast to the balconies, have ceilings.
- A legal heating device is possible only on loggias. But in this case, the space will become part of the total housing area.
- When arranging areas on balconies, it is required to take into account the level of permissible load.
Standard sizes


In typical houses, which became symbols of the 50-80s of the last century, balconies and loggias were "serial". In those days, design institutes developed sketches of future buildings according to standards. Then the concept of "standard balcony width" appeared.
In most cases, the balcony slab has the following parameters:
- Width equal to 3275 mm;
- The protrusion from the wall is 800 mm.
The slabs under the loggias are mainly:
- Width 5800 mm;
- The overhang is 1200 mm.
But the main fundamental difference between these two structures is that in the second type the slab is divided into two parts (2900 mm each) and separates two different apartments.
Note! The only exception is the corner type, in which the size changes due to the joining of two plates.
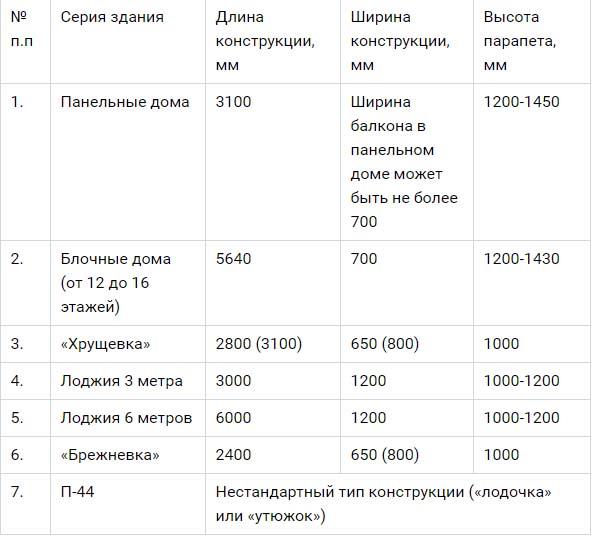
The table shows the standard dimensions of structures depending on the building series:

Another normative act regulates the size of balconies and loggias by geography. This is chapter 2.08.01-89 SNiP clause 3.2. The more severe the weather conditions in the climatic zone, the shallower the depth of the structure.
How to take measurements correctly
Usually the call of the measurer is free, and most likely this operation will be done by a professional. But you can also take measurements from the doorway yourself in order to order a product according to your own sizes. To perform a simple operation, you need to take a tape measure and chalk. You will also need a notebook and a pen to record your measurements.
Measurements are easier when there are no glasses in the frames.
We measure the height and width
First you need to measure the distance between the slopes. Next, the slopes are measured directly. Add the second to the first digit and subtract 4 centimeters. This will be the width of the future balcony block. The height is calculated in the same way. With these dimensions, you can go to a company that manufactures metal-plastic or wooden balcony blocks.
Measurement of a window with a door, as an integral structure, is performed a little differently.The width of the balcony door will be equal to the distance from the place where the window sill fits to the side edge of the slopes. And the height will be equal to the size of the gap from the window sill to the top of the slopes. If the glazing is not removed, the measurements will be approximate.
The most difficult case is when the opening width does not match at the top and bottom. Then, you may have to remove the wall, remove the too protruding part. This problem usually occurs if there was a distortion due to shrinkage of the building, or it was originally built unevenly.
Thickness measurement
Since modern buildings are built using new, often frame technologies, filled with porous materials, door thicknesses are usually less than the standard 7.5 centimeters. It is necessary to measure the depth of the opening where the box will be mounted. The thickness of the box, of course, must match this parameter.
Types of loggias and balconies and their sizes
The nature and national culture were so distributed that balconies and loggias in different countries have their own unique features. And many of them have successfully taken root in Russia and Ukraine.
- Style "Italiano" - designs of this type are distinguished by various forms and the use of multiple decorative techniques. Elegant, but complex forging is used as fences.
- "A la France" - this style prevails in the houses of the Soviet era. These are small structures that are more decorative than functional. Doors can be decorated with an elegant twisted lattice.
- Spanish Gothic - rectangular or square terrace with austere and laconic decor. The perimeter railings are framed with a concrete parapet or a modest lattice.
- Americano - structures of this type are located around the entire perimeter of the house, separated by thin bridges, the railings are lower than the standard. Relevant in individual buildings, hotels and tourism facilities.
- Portuguese veranda - found in low-rise construction, can be open or closed, in demand in preschool institutions and dispensaries.
- The Swedish balcony is the most common type of construction in our country. It differs in a narrow rectangular protrusion beyond the line of the facade; metal crossbeams are provided as fences. The parameters depend on the building series (see table).


The dimensions of such loggias completely depend on the type of building and the climatic zone. In the middle and northern latitudes, the protrusions of the structures are usually small. This allows you not to limit the passage of natural light. This is especially true in multi-storey construction, where the upper balcony space forms a shadow for the lower one. Loggias provide more shade, so they are smaller in the northern areas than in the southern ones.
Structural load
How can you find out how much weight a loggia can withstand in different houses? Any building has special calculations during its construction. These documents indicate how much the structure can be loaded, how many people can be on it. There are certain indicators for which you can make calculations and find out the necessary standards.
A separate SNIP has all the calculations of loads on certain structures. When calculating, it is necessary to take into account the full and reduced values of the requirements.
Taking into account the initial construction of the entire house, you can find out what the permissible load on the balcony will be:
Calculations
If citizens expand their living space on their own, then another question arises: what can be the maximum load on the balcony? In this case, you should pay attention to what year the house was built, as well as the quality of the building.
According to standard rules, the maximum load on the balcony slab can be 220 kg / km2. But, another indicator is established by law - 112 kg / m2.
The slab, which measures 0.8 x 3.2 m, is rated at 286 kilos. It is important to take into account the number of years of its use. After all, if it is already more than 40 years old, then the strength is lost by about 70%.Such structures should not be overloaded so that they do not collapse.
Glazing is an additional load on the balcony
Lately, fleeing from cold winters, many residents are glazing their balconies, and this is also an additional load. To make calculations, it is important to know the following indicators:
- The weight of the external finishing of the balcony is 1 r / m.
- Stained-glass window made of plastic, 1.5 m high and double glazing, weighing 55 kg.
- Siding with finishing elements per 1m2 - 5 kg.
- Plastic trim - 5 kg.
Given such indicators, the final load is obtained - 65 kilos, and the standard one is 50 kilos. It turns out that 15 kilos are extra. Therefore, before making calculations, it is necessary to make a preliminary inspection of the balcony. Light materials should be used for finishing: sandwich panels or siding.
On the loggias, which themselves have a lot of weight, glazing is extremely dangerous to perform.
We calculate the useful area
The main thing when calculating the area is access to the walls and the accuracy of the data. This will allow you to fit as accurately as possible into the budget planned for reconstruction or repair.
You will need the following tools:
- roulette;
- laser rangefinder;
- ruler;
- pencil;
- paper;
- calculator.
You can do without optics (laser rangefinder), but in some cases its use will allow you to avoid errors in the calculations. This is especially true for non-standard types of structures.
Then we follow the plan:
- To begin with, all sides of the figures that make up the balcony are measured. The parameters are immediately outlined.
- A sketch of the site is drawn on paper. The lines indicate dimensions.
- Calculations are performed on a calculator.
- The square is calculated by multiplying one side by itself.
- Rectangle - width multiplied by length.
- Triangle - The height is multiplied by the base.
- If the design consists of several forms, all the resulting calculations are added to each other.
- A reduction factor is applied 0.5 (for balconies), 0.3 (for terraces), 1 (for veranda). The resulting area of space is multiplied by this value.
Note! Appendix B, p. B. 2 SNiPu 31-01-2003 clearly regulates the area of open areas. The dimensions of the balcony are measured along the inner contour, not the outer.
The proposed plan is designed for self-measurement. If a beginner gets down to business, then errors are possible, especially in complex structures. If a team is invited for repair, then it is better to entrust the determination of the usable area to professionals. Most often this service is provided free of charge.
Definition and size of the balcony
A balcony, according to SNiP, is a platform protruding from the plane of the facade of houses. That is, the playground will be the defining difference between a balcony and a loggia. By and large, all flat horizontal structures that protrude beyond the wall of the house, while being at the floor level, are a balcony. That is, the parapet and roof of the balcony may be missing, but the floor should definitely be.
But the loggia is an independent room built into the building. That is, this structure has no protrusion behind the wall of the house. And the loggia also has three walls that are common with the building, two side walls and a roof. Only the front part remains open. There may be no glazing on the loggia.
Remember
On the issue of responsibility for the condition and repair of the balconies of an apartment building, managing organizations should remember the following:
- The composition of the common property of MKD includes not the entire balcony, but only the balcony slab (floor) and the load-bearing wall of the house.
- The MA is obliged to conduct inspections and monitor the condition of the common property of the house, including balcony slabs, and take timely measures to restore their proper condition.
- The MA must carry out routine repairs of balcony slabs at the expense of funds collected from residents of the house for the maintenance and repair of common property, regardless of whether an appropriate decision is made at the OSS.
- If the balcony slab requires major repairs, as evidenced by the inspection report, then the decision on the repair can only be made by the owners at the general meeting. In this case, the MA should carry out work as part of the current repair, if the overhaul is not planned in the near future.
- If the owners have not decided to overhaul the emergency balcony slab, then the management organization has the right to close and seal the entrance to the emergency balcony.
The managing organization should not ignore the complaints of the residents of the house about the condition of the balconies: if the structure collapses due to wear on the balcony slab, then the MA and its officials will bear responsibility for this.
What does SNiP mean: balconies and loggias, the height of the railing on the balcony
SNiP is a document that regulates the redevelopment and reconstruction of balconies. This is a collection of building codes and regulations. Loggia and balcony, according to this document, regardless of whether it is a cantilever type, closed or open, should not load the enclosing and supporting structures of the building where they are erected. Fire safety requirements, etc. are taken into account.


The creation of a balcony railing is an important step in equipping a balcony. The reliability and durability of the structure depends on whether the work is done well. According to the standards, it is allowed to use only one type of structure, which is listed as screen-type fences. And those elements that are used must withstand the loads established in SNiP.
The total height of the balcony railing depends on the height of the building. It should not be higher than 1000 mm at values less than 30 m, and 1100 mm at a height of more than 30 m. The minimum height of the handrail is 0.9 m. The handrail must have a high bearing capacity, higher than that of the staircase railings. In order to comply with safety regulations, the use of horizontal elements is prohibited. Installation of products with raw edges is also prohibited.
You may also be interested in the material on the restoration of balconies. When and where to start repairs, read our next article: https://homeli.ru/komnaty/balkon/restavratsiya-balkonov.
Operating rules
According to the established rules, it is not allowed to store heavy objects or debris on the balcony. The unauthorized building of the space between the balconies is also prohibited. To prevent leaks or freezing through the box, high-quality sealing and insulation must be performed. This can be done with foam rubber, felt or tow. To maintain sufficient temperature and humidity, the openings should be equipped with special polyurethane foam gaskets, which will need to be replaced after at least 5 years.
GOST dimensions: balcony slabs
Parameters, sizes, types of balcony slabs are regulated in accordance with GOST 25697-83. The slabs themselves are divided into several types: PB - solid flat beam, PBK - solid cantilever flat, PBR - cantilever ribbed. The length of the balcony slabs is from 1200 mm to 7200 mm, the width of the balcony slabs is 1200-1800 mm.


The thickness of typical balcony slabs in a brick house or panel house is in the range from 150 mm to 220 mm. It all depends on the type of slab, the size of the slab and the weight of the slab.
Expansion of the balcony structure along the base of the slab is possible. This concept implies the provision of additional usable space. But first, the loads of the balcony structure on the same slab are calculated in order to prevent its collapse. Usually, metal, steel brackets are used to expand the balcony.
Permissible loads
To perform accurate calculations, it is necessary to build on existing indicators. You can find out how much weight a kilogram of finishing or insulation can hold on the balcony, if, for the sake of order, take the load-carrying capacity of the loggia - 1770 kg. Distribute weight loads on several points:
- on average, three people weighing 80 kg is 240 kg;
- various devices and items - 175 kg;
- load of rainwater or snow - 200 kg.
It turns out that the non-glazed balcony receives a load - 615 kilos in our case.Given the indicator before glazing, the mass is 922.5 kilos. This means that for all materials in order to complete the decoration, 847.5 kilos are needed. For details of the competent finishing of the balcony, see this video:
Balcony norm-width and repair of balcony slabs
The width of the balcony in Khrushchev is 0.65-0.8 m, and the width of the balcony in the brezhnevka will be the same, but the length is less. In panel houses, the width is 0.7 m. And the loggia, three-meter or six-meter, will be 1.2 m wide. All these points, as well as other dimensions, are included in a document called a technological map. And all your changes, take the same example, expansion at the base of the slab, are entered into this map.
Along with other repair work, sometimes it is necessary to repair plastic doors on the balcony. You will find detailed instructions in our next material: https://homeli.ru/komnaty/balkon/remont-plastikovykh-dverej-balkona.


What does the repair of a balcony slab mean:
- It refers to a major overhaul, involving a large amount of work;
- Such repairs are carried out if the destruction of the slab has not yet reached the base, and the reinforcement has not been damaged by corrosion by more than 10%;
- The restoration process includes some transitional blocks - this is the cleaning of the slab, and the renewal of the reinforcement frame, and the installation of the formwork, and the concrete screed, and, of course, the strengthening of the parapet.
If the slabs have more significant destruction, these are already emergency slabs. They need to be replaced. If you yourself find that the slab is collapsing, contact the management company, write a standard statement so that the company creates a commission and draws up an act on the condition of the balcony. If it is recognized as emergency, this is already the work of the management company. That is, for example, what is in the apartment - doors, floor, you repair yourself. Any decor (if you want a stained-glass window on the balcony) - also yourself. But the balcony slab is already the responsibility of the managing party.
When the MA has the right to dismantle the balcony without the consent of the owner
In another case, the owner purchased an apartment in an apartment building and noticed that, contrary to the cadastral passport, there was no balcony in the building. The former owner of the apartment explained that the balcony was dismantled in his absence.
It turned out that the balcony slab was in disrepair, which confirms the inspection report. The inspection was carried out by representatives of the management organization and the municipality. In order to avoid the slab falling, it was decided to dismantle it. The UO complied with the decision.
The new owner demanded that the management organization restore the destroyed balcony. UO refused, citing the absence of a decision by the general meeting of owners of premises in the house to carry out major repairs. The owner went to court.
The court sided with the managing organization, since the commission that examined the balcony slab drew up an act on its emergency condition. Depreciation of structural elements was more than 50%, they could not be repaired or restored. In order to prevent the balcony slab from falling, it was dismantled. The work was carried out in the absence of the owner of the apartment, since no one lived in it for a long time.
The restoration of the balcony, as indicated by the court, refers to the overhaul of the common property of an apartment building. Such a decision must be made by the owners at the general meeting (clause 1, part 2, article 44 of the RF LC). The court rejected the claim and advised the owner of the apartment to initiate a general meeting of owners to make a decision on the restoration of the balcony slab at the expense of capital repairs.











