Even after a fleeting acquaintance with the copper and aluminum splendor displayed in the window, the owners of cast-iron batteries risk losing sleep and appetite.
But how, after all, to decide which radiator is better: copper or aluminum?
In this article we will weigh all the pros and cons and find out the winner.
Advantages and disadvantages of an aluminum radiator
Aluminum batteries are of two types:
- Cast: aluminum is better than other metals compatible with injection molding technology, which manufacturers successfully use. The cast radiator turns out to be one-piece, and therefore as durable as possible.
- Prefabricated welded: such batteries are made from a profile that is obtained by pressing an aluminum billet (extrusion method). Each section consists of two parts welded together. The radiator is assembled from several sections, fastened to one another by means of a thread. Such devices are less durable than cast ones.
The popularity of aluminum radiators is due to the following advantages:
- Great appearance.
- High thermal conductivity - the heat transfer of the section can reach 212 W.
- Light weight: with dimensions 80x80x380 mm, the section weighs only 1 kg.
- The product is guaranteed for a period of 10 to 20 years.
The strength of modern aluminum radiators, thanks to the addition of silicon, is quite acceptable: you can easily find a model designed for pressures up to 16 atm. And some manufacturers produce radiators that can operate at a pressure of 24 atm.


Aluminum heating coil
Aluminum batteries also have disadvantages:
- They do not like high temperatures - the coolant should not be hotter than 110 degrees.
- Corrosion susceptibility.
Prefabricated models cannot be used in systems in which antifreeze acts as a working environment.
What are aluminum and bimetallic radiators
Sectional aluminum radiators, that is, these are structures consisting of several ready-made separate ribbed sections made of one metal (in this case, aluminum) using casting or extrusion (powder metallurgy). In the first case, higher quality, albeit more expensive, products are obtained. The sections are connected to each other using nipples - connecting elements with an external thread on both sides. The tightness of the connections is ensured by gaskets.


Aluminum radiators
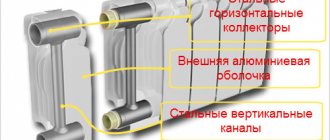
Bimetallic radiators can be either sectional or convection. Sectional ones in appearance and design are similar to aluminum ones, but if in those the section is solid, made of one aluminum, then in bimetallic ones it consists of a steel or copper core and an aluminum outer part (ribs).
Sectional bimetallic radiator steel + aluminum
Bimetallic convection-type radiators are a non-separable structure: a steel or copper tube, on which aluminum fins are perpendicularly "mounted" and all this is covered with an outer casing.


Bimetallic convection radiator copper + aluminum
Advantages and Disadvantages of Copper Heatsink
Today, for the manufacture of a copper radiator, only the purest copper is used: according to the technology requirements, the amount of impurities should not exceed 0.1%. This approach provides the following benefits:
- High thermal conductivity of the material, resulting in an equally high heat transfer.
- Good durability, allowing the device to work in systems with high pressures - up to 16 atm.
- High corrosion resistance.
- The ability to maintain working qualities at coolant temperatures up to 250 degrees.
It is possible to connect a copper radiator to the pipeline either by means of a threaded connection or by means of soldering. Thanks to this versatility, the cost of installation work can be significantly reduced.


Copper heating radiator
Another important advantage of copper is its high ductility at low temperatures. If a filled heating system freezes, then the copper elements will only deform, but will not burst.
Copper radiators, unlike steel appliances, are not afraid of the effects of chlorine salts, which are very often found in quite abundant quantities in our heating systems.
All of the listed advantages determine the durability of this type of heating devices.
At the same time, the buyer should take into account some disadvantages:
- High cost - a copper radiator costs about 4 times more than a steel one.
- Simultaneous connection of such devices with galvanized steel pipes in the direction of movement of the working medium is not allowed - the electrochemical reaction that occurs in this case can cause destruction of the material.
- It is undesirable to use copper batteries in systems where the coolant contains a large amount of hardness salts or has a high acidity.
Problems can be avoided if copper batteries are connected to steel pipes using brass adapters.
Comparison of characteristics
Almost all of the products discussed above are distinguished by a modern, rather aesthetic appearance and fit well into the interior of a modern house or apartment. But, all the same, which one is better and which one to choose? In order to determine which of the radiators is better for each specific case: aluminum or bimetallic, sectional or convection, we will consider and compare their characteristics and features of operation.
Thermal conductivity and heat transfer
Aluminum radiators are characterized by very good thermal conductivity and low thermal inertia. Due to the presence of fins, the heat transfer of one of their sections can reach 200 W or more. They heat up very quickly, but also cool down quickly. Air heating in the room occurs both due to direct radiation and convection.
The heat dissipation of bimetallic batteries is usually somewhat lower and depends on the metal used in tandem with aluminum. Products with a steel core have the lowest (20-25% lower than that of aluminum ones). If the core is made of copper, then the heat transfer will be almost the same as that of aluminum.
Convection-type bimetallic radiators require more time to heat the room, since it occurs mainly due to air convection. But on the other hand, such products are safer, especially if there are small children in the house. Their outer casing heats up slightly and you can not be afraid that you can get burned, for example, from accidentally touching a very hot battery.
Heating medium circulation
According to this indicator, aluminum radiators have an advantage. The internal space of their sections is larger than that of bimetallic ones (both sectional and convection) and therefore less resistance to the circulation of the coolant is created. In addition, the thin core tubes of bimetallic batteries can clog faster.
Ability to withstand pressure and water hammer
According to this indicator, bimetallic radiators have the best characteristics.They can withstand more pressure (more than 20 atm.), In comparison with aluminum ones (usually up to 16 atm.), And easily cope with water hammer in the heating system, which cannot be said about products made of aluminum alone. This is especially true for houses or apartments that are connected to a central heating system.
Interaction with aggressive coolant
Although aluminum is a fairly corrosion-resistant metal, it can still react with various additives and additives that are present in the coolant, especially circulating in the central heating system. And if its pH (acidity) is still more than 8, the liquid circulating in the section can quite "eat through" it from the inside and rather quickly.


Sectional bimetallic radiator copper + aluminum
Bimetallic radiators, in this case, have an advantage. Even if the core is made of ordinary (black) steel and is susceptible to corrosion, the effect of aggressive coolant additives on it, nevertheless, will not be as strong (especially if it is covered from the inside with special protection) as on aluminum. Another thing is when the coolant is drained from the system, then in this case the steel core will be subject to rapid corrosion, and this is not a problem for aluminum.
The greatest advantage, according to this indicator, has bimetallic radiators, the cores of which are made of stainless steel or copper. But this option is also the most expensive one.
True, in autonomous heating systems, where the quality of the coolant can be controlled, this criterion is not decisive.
Life time
The service life of aluminum radiators can reach 25 years and is mainly determined by the quality of their manufacture and their operating conditions (quality of the coolant, pressure and presence of water hammer in the system).
The service life of bimetallic radiators can be practically the same and even longer. Besides the same workmanship, it depends on the type of metal used for the core. It is the smallest (no more than 20 years) for radiators with steel cores (especially unprotected from the inside), and then, provided they are used correctly, and the largest - with copper or stainless steel (25 years or more).
Installation
In principle, it is quite simple to install both those and other radiators using standard fittings, choosing them depending on the type of pipes used for wiring. The only difference is that the metal of the core of bimetallic batteries is stronger than aluminum and by connecting them to pipes you can not be afraid to damage the threads. In addition, if the distribution of the heating system is made of steel pipes, then, in order to prevent the occurrence of electrochemical corrosion at the junction, an adapter not made of "black" steel must be installed between the aluminum battery and the pipe.
The cost
In terms of cost, most aluminum radiators are cheaper than their bimetallic counterparts. True, we are talking here about high-quality products, and not about cheap, but low-quality products, most of which come to us from China. Such products, although they are similar in appearance, will not last long, regardless of whether they are aluminum or bimetallic. In addition, they can present an unpleasant surprise at the height of the heating season.
Which heater radiator is better: copper or aluminum?
As you can see, copper and aluminum radiators are very similar to each other. They are lightweight and have excellent design and increased heat dissipation. The latter quality allows the user to reduce the volume of the heating circuit and apply the temperature regime 80/60 (supply / return) instead of 90/70 without increasing the area of the radiators.
Both types of radiators, due to their low heat capacity, have low thermal inertia, which allows the boiler to remain in optimal mode during warming outside.


Aluminum batteries in the interior
At the same time, both copper and aluminum are soft metals, and therefore they do not tolerate the presence of solid mechanical impurities in the coolant that have an abrasive effect.
At the same time, one cannot fail to notice that aluminum radiators are in many ways inferior to copper ones. We have already said above that high temperatures are contraindicated for them. To this can be added the ability to self-air: specific chemical processes lead to the formation of air locks, which must be vented from time to time.
Prefabricated aluminum radiators do not tolerate water hammer that occurs in heating systems during a sharp change in weather.
In addition, with frequent changes in temperature conditions, aluminum in contact with steel suffers from a significant difference in the coefficients of thermal expansion of these materials. For this reason, they are best used in regions with consistently cold winters.


Powerful copper heatsink
And the last thing is corrosion. In the heat supply conditions usual for us, aluminum is short-lived - it needs a coolant with a pH of 7 or 8.
Thus, copper radiators can be considered less moody.
It would seem that there are many varieties of heating batteries, but new items are still appearing. Vacuum heating radiators: device and varieties, as well as prices for devices.
You can find an overview of manufacturers of cast iron heating radiators here.
And in this article, https://microklimat.pro/sistemy-otopleniya/montazh-sistem-otopleniya/sxemy-podklyucheniya-radiatorov.html, the diagrams for connecting heating radiators are presented, as well as recommendations for the place of their installation.
Aluminum properties


Aluminum wiring bends easily but breaks quickly
Aluminum belongs to the category of light, chemically and biologically inert metals with a specific gravity of 2700 kg / m³. The material is safe for humans and the environment.
Advantages of aluminum:
- Affordable cost. The price is determined by the lower melting point and lower production costs than other metals.
- Plastic. The wire bends well, keeping its shape. The conductors are given any configuration required for operation.
- Formation of a protective layer. After cleaning, the surface of the metal is covered with a thin layer, which prevents its oxidation throughout the entire volume.
However, aluminum has the following disadvantages:
- High resistance to electron flow. This causes the lines to heat up, which can ignite the finishing materials.
- High level of thermal expansion. This leads to a weakening of the contact connections. With frequent switching on and off of lines with high load, the circuit is disconnected.
- Oxidation on contact with air. The resulting film has poor conductivity, due to which the contacts overheat and melt the insulation, and the "ground" line simply ceases to fulfill its function.
- Short service life. He does not exceed 30 years with an average load.
Today, in accordance with the requirements of GOST, the use of aluminum is prohibited in the construction of residential buildings and engineering structures.
Testimonials
When studying the discussions on the pages of online forums, no complaints about copper or aluminum radiators were found.
True, not many can afford copper radiators - the price of a device designed for heating 20 - 25 sq. m, reaches 23 thousand rubles.
Due to such a high cost, such devices have not become widespread, so there are many false rumors about them.
For example, some have expressed concern that copper will turn green, as happens with copper roofs or monuments.
Connoisseurs reassure: a greenish oxide (patina) is formed only with prolonged exposure to high humidity.
Many people consider aluminum batteries to be too light and unreliable, but they are being used more and more often.Aluminum heating radiators: technical characteristics, advantages and disadvantages, as well as types of structures.
Why do you need a thermostat for a heating radiator, how to install it and which one is better to choose, read in this topic.