Types of structures
Heating circuit - elements used as a heating system by transferring heat energy into the air. The most popular systems are those that use boilers as a heating source, boilers with a connection to the water supply. The liquid, crossing the heating elements, reaches the set temperature, heading to the heating circuit.
The movement of the coolant is provided by two methods:
- natural;
- forced.
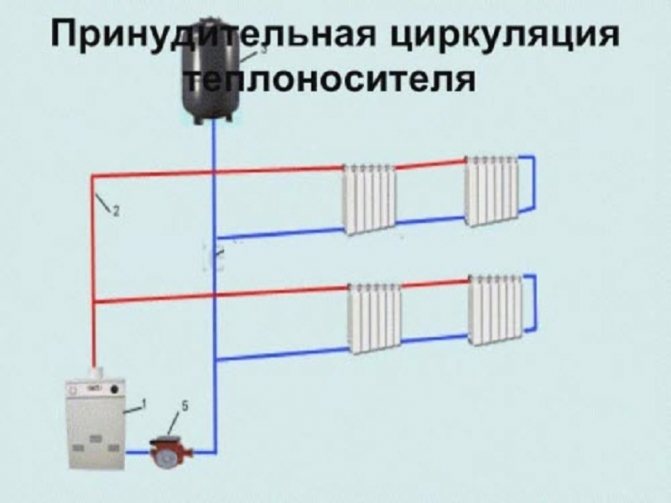
Forced circulation through pipes
Systems with natural movement of the coolant are simple and reliable. Efficiency depends on the correct structure of the heating circuit. In the latter case, a pressure-generating pump is introduced. The coolant moves through the pipeline.
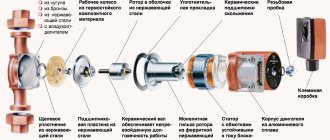
Heat sources for heating liquid - boiler, boiler equipment. The mechanism of work is based on the conversion of one type of energy into heat. Depending on the raw materials, heating source, boilers operate on gas, solid fuel, electricity, and fuel oil.
All types of boiler units can be used to heat a private house. Gas, solid fuel devices are popular.
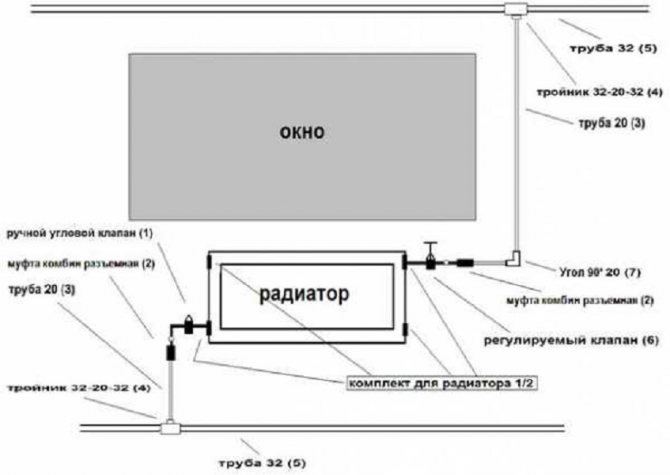
Depending on the connection of heating devices in the heating circuit, a distinction is made between one-pipe and two-pipe systems. One-pipe system - when the batteries are connected in series, water, crossing each element, returns to the boiler.
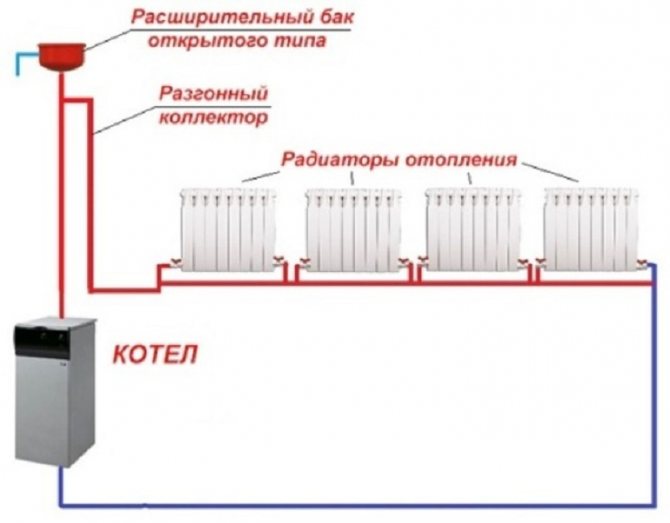

One-pipe scheme
Minus - uneven heating of the room. Each subsequent radiator receives less heat energy.
In a two-pipe heating circuit, the batteries are connected in parallel with the riser. The negative side of the system is the complexity of the design, high material consumption. In multi-storey buildings, only a two-pipe heating system can be used.
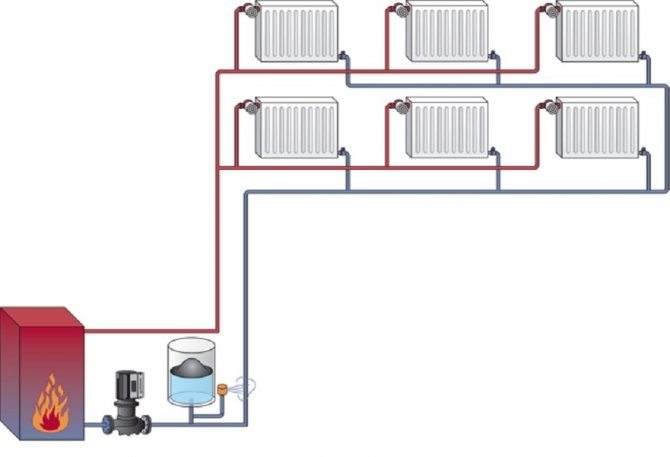

Two-pipe scheme
When you can not use the pump
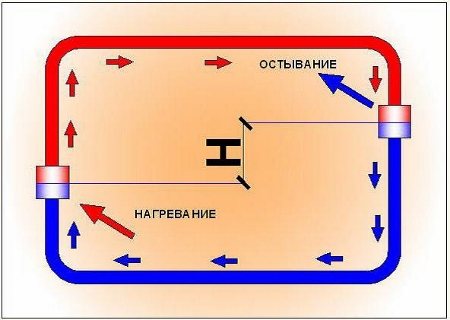

How natural circulation heating works (click to enlarge)
The principle of operation of a heating system without a pump is based on the movement of fluid under hydrostatic pressure. In other words, the liquid in the heated state has a lower density than the cooled one, therefore the top rises, thus promoting the circulation of the coolant in the system.
As a rule, heating with natural circulation is installed in country cottages and country houses. This is due to the fact that in such living quarters there are very often power outages, or even none at all, as a result of which it is impossible to install heating with forced circulation.
A distinctive feature of this heating system is that it is very easy to use, and you can install it yourself.
Heating without pump
Previously, the design of water heating systems was carried out without circulation pumps. The difficulty arose when buying, installing devices that cause forced circulation of water in the circuit. When foreign manufacturers appeared on the market, the situation changed dramatically. Circuits with forced circulation of a heat carrier are more often used.
Failures in the supply of electrical energy have not been eliminated everywhere.
As soon as the electricity is cut off, the water circulation stops. The room is cooling down. The batteries get cold. The heating system is not working efficiently. The water in the circuit freezes. It is required to start the source of thermal energy.
Advantages disadvantages
From a technical point of view, natural water circulation is effective in tall buildings.The reason is the properties of the fluid in transferring pressure from the surface to the circuit to the lower unit.
The advantage of gravitational water circulation is saving building materials. Expensive pumps, electrical supply to the circuit are not needed. Any man can design, install, operate the system. There is no need to pay for the services of the master. With proper construction, the system will heat the house for a long time, efficiently. Major repairs will not be required for more than 30 years.
The scheme of natural water circulation assumes a self-regulation process. The heating system is characterized by high thermal stability.
Disadvantages:
- high level of inertia;
- exposure of regulated pipe slopes during installation;
- the use of pipes of large cross-section;
- high probability of freezing due to poor water pressure;
- airing of heating devices.
Air bleed devices will be required to correct the air problem in the batteries. An expansion tank is installed in the system to control the water level in the boiler.
Natural circulation of the coolant in the pipes:
Operating principle
The law of physics: after heating, thermal energy increases in volume, losing its previous density. The unit in which heat is exchanged between the source and the carrier is a heat exchanger.
The heated liquid is lighter than the cooled one, the heat generator is placed at the bottom of the heating circuit. The slightly warmed up heat carrier moves upward. In its place, cold water descends through pipes. In the case of natural circulation in the system, three physical laws are considered: friction, expansion of bodies with increasing temperature, and the continuity of the jet.
The structure of the water heating circuit with natural circulation of the coolant includes:
- Heat generator - boiler. Water is heated in the heat exchanger.
- Pipes. Form the direction of water movement. The pipeline is supplied to boiler equipment, radiators.
- Heating devices - radiators in different designs (differ in shape, material).
- Expansion tank. Protects at the stage of compensating for the increase in fluid volume due to thermal expansion. Installed at the top of the heating circuit.
The simplest scheme without a pump - the heated coolant moving through the pipes leaves the boiler, the chilled water flows back. Vicious circle.
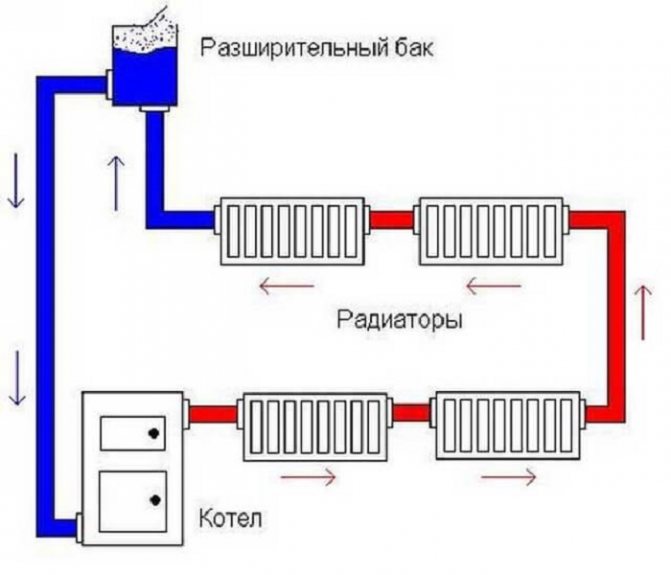

Water circuit diagram without pump
Having flowed up the system, the water begins to be distributed to the radiators. Processes opposite to circulation in boiler equipment are observed. Displacing the cooled liquid, the coolant fills the radiator. Water gives off heat to the battery. Thermal energy enters the air, warming up the room. The liquid cools down and circulates towards the boiler. The process is cyclical.
Single-pipe heating
The difference between one-pipe schemes is efficiency. Systems are rarely used. The heated coolant, rising through the pipes, sequentially passes the batteries located on the second floor. Heading down the pipes, there are radiators located on the lower floor. Returns to the boiler.
The temperature of the upper floors of the house is higher than in the apartments on the ground floor. For sufficient circulation of liquid through the pipes, a high performance heating element is required. For private houses, the scheme is suitable in terms of efficiency, quality of heating the premises.
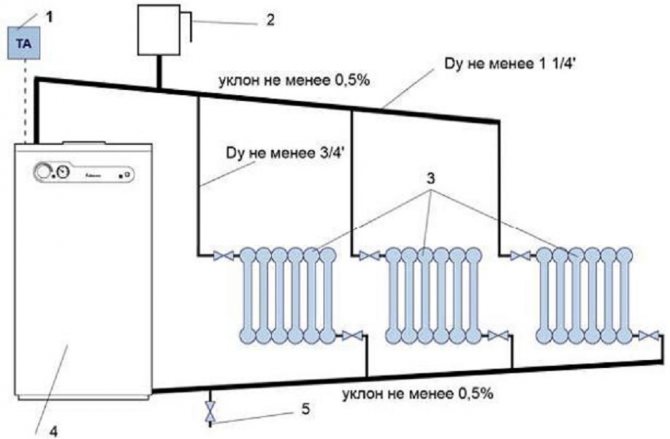
The system can be made more efficient by the additional introduction of a bypass line - bypass. A closing section is made from the pipe. The diameter of the material must not exceed the dimensions of the pipeline. The bypass connects the inlet, outlet of the radiator. It is connected to a T-piece at the top of the heating circuit, in front of the expansion tank. Divides the circuit into two parts.
The correct mechanism for the operation of the heating circuit depends on the expansion tank. Dimensions - on the number of batteries.More than three quarters of the total volume should not be filled.
In a private house, it is better to make a vertical pipe connection. Installation of two risers is in progress: lifting, lowering. The installation of an expansion tank is not required if you make an automatic bleeding system for each battery, which accumulates at the top of the convector.
Two-pipe heating circuit
The two-pipe scheme eliminates the problem of uneven heat distribution. Two circuits are introduced at once. The first is responsible for the circulation of hot water from the source to the radiator. The second is for the outflow of the remaining liquid.
Methods for connecting pipes: with passing circulation, dead-end. The passing movement is characterized by the creation of battery taps of the same length. Uniform heating is maintained. The scheme did not gain popularity due to the high consumption of building materials (pipes).
Preference is given to a connecting scheme with cold, hot water circulation in different directions. Batteries that are closer to the heating device warm up faster.
The heating scheme is divided according to the type of pipe layout. Heated water is supplied from the basement, basement. The return line is located just below the feed unit.

Scheme with the upper piping of heating pipes
What is important to know?
The wiring diagram and methods for connecting a device such as a circulation pump to electricity can be of various designs. The choice of a specific option is determined by the characteristics of the heated object, as well as by the place where the device is located. There are two ways to connect it:
- direct connection to the 220 V power grid;
- connection to an uninterruptible power supply, which in turn is connected to a 220 V or 220/380 V network (in the case of a three-phase UPS).
Choosing the first method, the consumer runs the risk of being left without heating in the event of a prolonged power outage. This option can be considered justified only with a high degree of power supply reliability, which reduces the likelihood of a long power interruption to a minimum, as well as, if there is a backup source of electrical energy at the facility. The second method is preferable, although it requires additional costs.
System installation
When designing a water-type heating circuit without a pump, you need to correctly position the boiler, the lower radiator. The higher the battery in relation to the boiler equipment, the worse the outflow. Heating devices are best installed in the basement. The circulation rate of the coolant is affected by:
- section of pipes. With a decrease in the diameter of the pipeline, the resistance to the coolant increases;
- pipe material. It is better to use polyurethane products;
- number of bend points. With a decrease in the quantity, the efficiency of the heating circuit increases. Performance depends on the number of valves.


Installation work
To calculate the power of boiler equipment, you need to apply the recommendations of SNiP. For one square meter of the heated room, a heating element with a capacity of 0.1 kW is needed. When installing the heating unit, it is necessary to insulate the hot water riser, the room with the expansion tank.
Installation work: install the main riser. An expansion tank is mounted on top. Connect the wiring at the level of 1/3 of the room height from the floor. Pipes are diverted to radiators. One-pipe wiring involves connecting pipes to the boiler from the last radiator. Two-pipe - parallel connection of batteries, tie-in of branches into a common pipeline.
Steam use
The heat carrier can be water, steam. Steam generators are installed to convert water into steam, supplied through pipes.
Mechanism: hot air is lighter than chilled air. The heated steam quickly moves up the heating unit. Artificial heating is not required. When entering the batteries, the gas is cooled. It turns into a liquid state.Returns to the boiler again.
Heating systems of a liquid type without a pump are popular. This applies to projects of private, country houses. It is important to make calculations. This will protect against freezing in the cold winter.