Disadvantages of a closed heating system
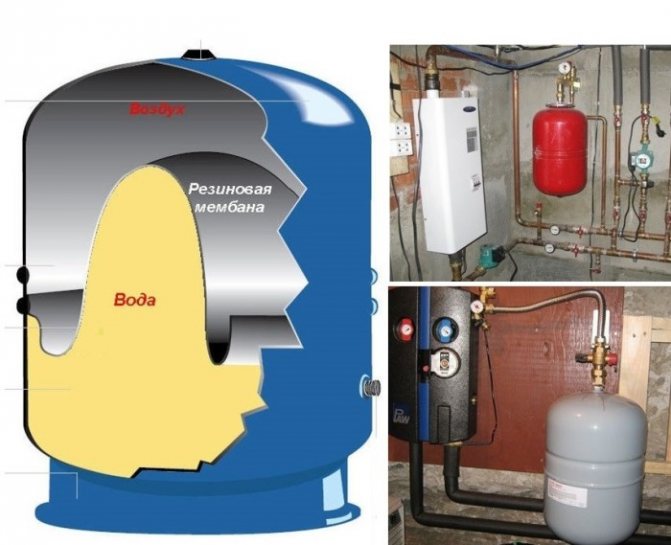
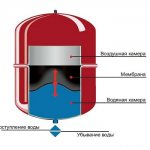
Diaphragm expansion tank
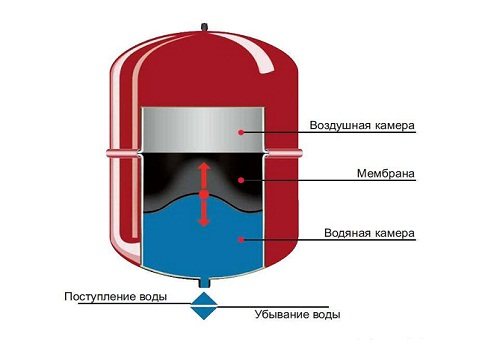
The disadvantage is the presence of a diaphragm expansion tank, which must have a large volume. A tank is selected with the expectation that its volume should be equal to 0.03 of the total volume of the heating system. The tank is filled only by 0.3-0.6 of its full volume, the remaining volume remains for a possible increase in the volume of the coolant. It should also be borne in mind that the larger the heating system, the less filling the expansion tank. The diaphragm expansion vessel in the heating system serves to maintain the pressure at certain values.
Another drawback is that the circulation of the coolant is forced, therefore, when the electricity is turned off, the operation of this system is not possible.


Closed heating system photo
Alas, all the "pitfalls" associated with design flaws, poor quality materials or illiterate installation will begin to appear gradually. And if errors in the project or inadequate quality of materials can be identified even before the start of work, then the installation process is very difficult to control. To be sure of the quality, you need, at least, to be an installer yourself and observe the process of installing heating devices from the first to the last second.
However, most of the typical flaws that can later become the cause of serious trouble are easy to identify. Our small review of errors and misconceptions will be devoted to them.
Calculation and selection
The device or modernization of the heating system begins with the design. It is necessary to immediately make a reservation that in a city apartment connected to centralized heating, there are very few opportunities for transforming the existing system and you can do without it. You can replace the pipes with more modern ones and change the radiators for more efficient and beautiful ones.
There are much more possible options for heating schemes in a private house or cottage. Accordingly, the design should be approached much more responsibly. Moreover, ideally, the project should be ready even before the start of the construction of the house.
First of all, based on the area of the building, its layout, the height of the ceilings, as well as the type and thickness of the walls, the required boiler power, the optimal type of fuel (gas, electricity, diesel fuel, etc.) are calculated. At the next stage, pipe layouts, the location and type of radiators and other aspects are developed.
Already at this stage, a number of mistakes are possible, which will inevitably turn into problems. As you know, heating systems are available with natural or forced circulation. In systems with natural circulation (gravity circuit), the coolant (water or a special liquid - antifreeze) circulates through pipes and heating devices due to its different densities in the supply (hot) and return (cold) lines. In systems with forced circulation, water moves through pipes and radiators due to the operation of circulation pumps. Both systems have their own characteristics that affect the nuances of design and selection of components.
First of all, a system with natural circulation does without a pump, which means it does not depend on the availability of electricity.But due to design features, it is suitable only for small one-two-story houses with an area of up to 100-150 sq. In addition, this archaic system can only be regulated by increasing or decreasing the boiler output. In addition, in order for the gravitational scheme to work without difficulty, in such a system it will be necessary to use more expensive pipes with a large cross-section (at least 50 mm), and when laying out, strictly observe the slope angles. As a result, the cost of materials for arranging a home heating system almost doubles.
You can add one more to the list of features. In systems with natural circulation, as a rule, an open expansion tank is installed, which is needed to compensate for the thermal expansion of the coolant. So the coolant is in direct contact with atmospheric air and is constantly saturated with oxygen. This leads to the fact that steel pipes and radiators are corroded much more intensively. Therefore, in such systems, only heavy and unaesthetic cast iron radiators, which are especially resistant to temperature extremes and oxygen, can be safely used. You will have to forget about modern and efficient heating devices.
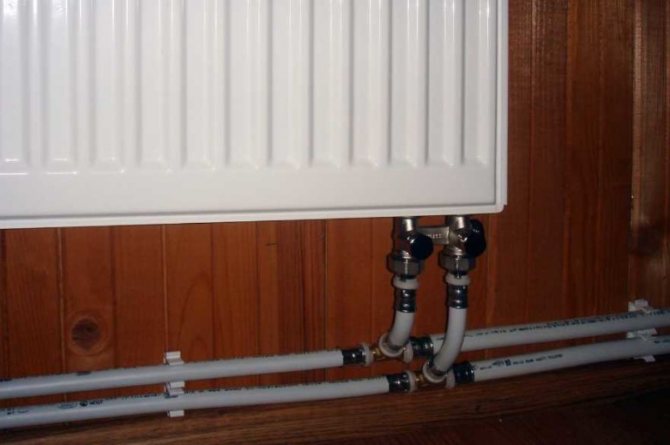
The most common systems with a circulation pump now allow the use of pipes with a smaller cross-section, and, therefore, in the end, turn out to be more "economical". In addition, as a rule, they are of a closed type, that is, they use membrane expansion tanks in which the coolant does not come into contact with atmospheric air. This allows you to use all the variety of modern heating devices - bimetallic and aluminum radiators, steel panel and tubular radiators, and finally, design radiators.
However, here, too, the problem of dissolved oxygen and corrosion does not cease to be relevant. If, according to domestic standards, the oxygen content in the coolant should be no more than 0.02 g / l, then in practice both in centralized systems and in autonomous (with intensive feeding) this value is ten to twenty times higher. Therefore, it is reasonable to use modern corrosion-resistant radiators, for example, such as a tubular steel radiator Charleston Pro (developed by Zehnder) with a special internal anti-corrosion coating.
Installation pitfalls
As already mentioned, installation flaws do not appear immediately. They are often difficult to notice even for a specialist “on the spot”. Disadvantages manifest themselves at the most inopportune moment - during the heating season. They are manifested, as a rule, by coolant leaks and a decrease in the power of the system, due to which the dwelling does not receive the required amount of heat.
The main mistakes of the installers, for which the customer then pays, are quite typical.
Wrong Tool Error
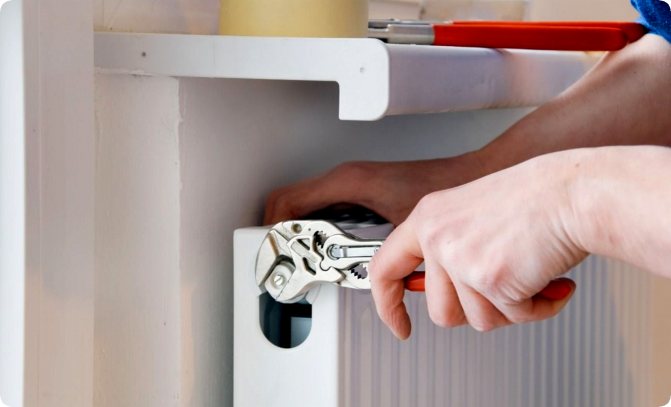
One of the most common problems is that installers do not have the right tools or they are of poor quality. The main tools used in the installation of heating systems are an adjustable and "universal" gas wrench. But for the installation of systems using modern materials, such a set will not be enough. The installer's “ideal kit” should include the following tools: an adjustable wrench, a good quality gas wrench, a special wrench for reinforced plastic pipes, a special step wrench for detachable connections.
The catch is that good tools from Swedish and German brands (such as REMS, Rothenberg, Fulco, Forged) are not cheap - just a gas wrench costs about 40 euros. Cheaper counterparts may be of inadequate quality, for example, mild steel, which does not withstand stress.As a result, the installer, “sparing” the tool, may “fall short” of the threaded connections, which sooner or later will lead to coolant leaks, and, possibly, to a breakthrough in the system.
It also happens that a completely wrong tool is used that is needed. For clarity, we will give one example. All modern radiators are equipped with thermostats - rather complex mechanisms that allow you to control the radiator and, consequently, the temperature in the room. Now imagine a fitter armed only with a gas wrench and a sledgehammer. With such a minimum set of tools, it is very difficult to correctly install the thermostat, since the prescribed efforts are not respected, there is a high probability of ripping off the thread or deforming the parts of the device. This threatens that one day the connection will not withstand the pressure in the system and the heating will "flow".
Right angle error
Another common misconception among customers and installers is that radiators must be installed strictly horizontally. Indeed, how could it be otherwise? But it turns out that the radiators should be installed at a slight slope. In radiators hanging strictly horizontally, air gradually accumulates - it simply has no "outlet", and it periodically has to be vented manually, through a special "air" valve. But the owners do not always remember this. As a result, the power of the heater, although not much, is reduced.
Error "Wrong sealants"
As you know, pipe connections, especially threaded ones, need to be sealed. Previously, flax was widely used as a sealant. Today linen thread is also used, but on rare occasions. The most popular modern sealants are heat-resistant silicone and special Teflon thread (for example, produced by Wineflon).
Unscrupulous installers use a variety of materials as a seal, which are not intended at all for this. For example, they can take a cheaper silicone for plastic windows, which is designed for a completely different temperature regime. Of course, outwardly such a connection will look quite normal. But once the heating system is working, the sealant will not withstand the high temperatures. And this is fraught - if not a breakthrough in the system, then at least a coolant leak.
Error "Wrong coolant"
Often, autonomous heating systems are filled not with water, but with more frost-resistant heat carriers that do not freeze at negative temperatures. But the use of antifreeze as a coolant imposes a number of technical features on the performance of the heating system, which are not always taken into account. So, special requirements are imposed on the used sealants and gaskets. For example, common rubber gaskets for cast iron radiators "swell" and lose their properties when exposed to ethylene glycol based antifreeze. This leads to leakage of the heating medium.
In general, experts strongly discourage the use of antifreeze. The fact is that heating boilers are designed for the thermophysical properties of water (thermal conductivity, viscosity, etc.), and the properties of antifreeze are very different, so that the probability of emergency shutdowns of the boiler due to overheating or even premature failure of the heat generator increases.
Error "On the market is cheaper"
Another mistake concerns installers and homeowners alike. It stems from an obvious desire to save money. The fact is that for the reliable operation of the system, good shut-off valves are required - gate valves, ball valves, etc. And the domestic market is rich not only in various models of ball valves, but also in equally diverse fakes for branded products. And if the installer or the homeowner himself wants to save on a branded ball valve by buying it two or three times cheaper, then it will probably turn out that the crane is a fake.It is made of cheaper and more fragile materials, softer, and, therefore, will fail much earlier than the "proprietary" fittings.
On average, it will take about 100 euros to complete the radiators with high-quality fittings. If you try to save money, the risk that the heating system will break through on a winter evening lies entirely with the owners.
In search of competence
In general, the situation in the field of heating installation services remains difficult now. Sometimes the professional level of installers is insufficient to work with modern materials and equipment, which require completely different techniques that differ from traditional ones.
Homeowners planning to install or modernize the heating system in their home can be advised to be more careful about the choice of not only components and materials, but also the company that will be engaged in the installation. And, of course, do not rush to entrust such a responsible business to “folk craftsmen”, “wild brigades”, because the funds saved at this stage can turn into many times greater losses in the future.
As for the companies involved in the installation of heating systems, ask her representative to give you a short tour of the facilities, which were carried out by the specialists of this company. Find out how many years the system has been in operation, evaluate the quality and thoroughness of the work performed. After that, it will be much easier for you to decide whether to trust this organization or it is better to look elsewhere.
Prepared by the press service of the Russian representative office of the Zehnder Group
Source: https://www.lim-climat.ru
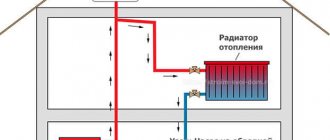
How a closed heating system works
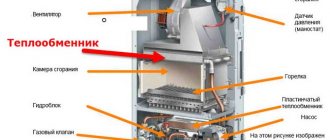
Heating of the coolant to the required temperature occurs in the boiler. After that, due to the circulation pump, the coolant circulates through the system. When heated, the coolant expands and increases in volume, which leads to an increase in pressure in the heating system. All excess volume of the coolant enters the expansion tank, which is what regulates the pressure.
But the options are not excluded that the pressure range will be exceeded and, in order to avoid rupture of the radiator, a safety valve is installed through which, in a critical situation, the coolant will be discharged. The room is heated through a heating device through which the coolant circulates. The filter removes suspended matter and dirt from the system. Despite the fact that the system is closed, the possibility of air entering the coolant is not excluded, and air can also enter the system after flushing the heating system.
The automatic air valve does this very well. Also, to ensure the operation of the heating system, it is necessary to provide for feeding the network from the water supply, and if the pressure of the water supply is not enough, then it is necessary to install a make-up pump.
If you have any questions about a closed heating system, ask them in the comments, I will be happy to answer.
Heating characteristics
Depending on the predominant heat transfer method, space heating can be convective and radiant
.
Convective heating
A type of heating in which heat is transferred by mixing volumes of hot and cold air. The disadvantages of convective heating include a large temperature difference in the room (high air temperature at the top and low at the bottom) and the impossibility of ventilation of the room without loss of thermal energy
Radiant heating
A type of heating when heat is transferred mainly by radiation and to a lesser extent by convection.Heating devices are placed directly under or above the heated area (built into the floor or ceiling, they can also be mounted on walls or under the ceiling) [3] [4].